Liposomal Nanomedicine: Applications for Drug Delivery in Cancer Therapy
- PMID: 34032937
- PMCID: PMC8149564
- DOI: 10.1186/s11671-021-03553-8
Liposomal Nanomedicine: Applications for Drug Delivery in Cancer Therapy
Abstract
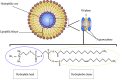
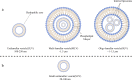
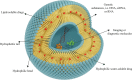
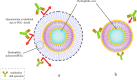
The increasing prevalence of cancer, a disease in which rapid and uncontrollable cell growth causes complication and tissue dysfunction, is one of the serious and tense concerns of scientists and physicians. Nowadays, cancer diagnosis and especially its effective treatment have been considered as one of the biggest challenges in health and medicine in the last century. Despite significant advances in drug discovery and delivery, their many adverse effects and inadequate specificity and sensitivity, which usually cause damage to healthy tissues and organs, have been great barriers in using them. Limitation in the duration and amount of these therapeutic agents' administration is also challenging. On the other hand, the incidence of tumor cells that are resistant to typical methods of cancer treatment, such as chemotherapy and radiotherapy, highlights the intense need for innovation, improvement, and development in antitumor drug properties. Liposomes have been suggested as a suitable candidate for drug delivery and cancer treatment in nanomedicine due to their ability to store drugs with different physical and chemical characteristics. Moreover, the high flexibility and potential of liposome structure for chemical modification by conjugating various polymers, ligands, and molecules is a significant pro for liposomes not only to enhance their pharmacological merits but also to improve the effectiveness of anticancer drugs. Liposomes can increase the sensitivity, specificity, and durability of these anti-malignant cell agents in the body and provide remarkable benefits to be applied in nanomedicines. We reviewed the discovery and development of liposomes focusing on their clinical applications to treat diverse sorts of cancers and diseases. How the properties of liposomal drugs can be improved and their opportunity and challenges for cancer therapy were also considered and discussed.
Keywords: Cancer treatment; Drug delivery; Liposomal drugs; Nanomedicine; Therapeutic nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Recent advances and clinical translation of liposomal delivery systems in cancer therapy.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2024 Feb 1;193:106688. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2023.106688. Epub 2024 Jan 1. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2024. PMID: 38171420 Review.
-
Advanced targeted therapies in cancer: Drug nanocarriers, the future of chemotherapy.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015 Jun;93:52-79. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2015.03.018. Epub 2015 Mar 23. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015. PMID: 25813885 Review.
-
Approaches to Address PK-PD Challenges of Conventional Liposome Formulation with Special Reference to Cancer, Alzheimer's, Diabetes, and Glaucoma: An Update on Modified Liposomal Drug Delivery System.Curr Drug Metab. 2022;23(9):678-692. doi: 10.2174/1389200223666220609141459. Curr Drug Metab. 2022. PMID: 35692131 Review.
-
[Development of antituberculous drugs: current status and future prospects].Kekkaku. 2006 Dec;81(12):753-74. Kekkaku. 2006. PMID: 17240921 Review. Japanese.
-
Promising Nanomedicines of Shikonin for Cancer Therapy.Int J Nanomedicine. 2023 Mar 10;18:1195-1218. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S401570. eCollection 2023. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023. PMID: 36926681 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nanomedicines in diagnosis and treatment of prostate cancers: an updated review.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Aug 21;12:1444201. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1444201. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39318666 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress and prospect of nanotechnology for cardiac fibrosis treatment.Interdiscip Med. 2023 Oct;1(4):e20230018. doi: 10.1002/INMD.20230018. Epub 2023 Sep 5. Interdiscip Med. 2023. PMID: 38089921 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Updates on Responsive Drug Delivery Based on Liposome Vehicles for Cancer Treatment.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Oct 15;14(10):2195. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14102195. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36297630 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanocarrier cancer therapeutics with functional stimuli-responsive mechanisms.J Nanobiotechnology. 2022 Mar 24;20(1):152. doi: 10.1186/s12951-022-01364-2. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022. PMID: 35331246 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multifunctional nanoparticle for cancer therapy.MedComm (2020). 2023 Jan 11;4(1):e187. doi: 10.1002/mco2.187. eCollection 2023 Feb. MedComm (2020). 2023. PMID: 36654533 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wild CP, Stewart BW, Wild C (2014) World cancer report 2014. World Health Organization Geneva, Switzerland
-
- Organization WH: Cancer. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer (2018). Accessed 12 Sep 2018
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

