Brazilian version of "The Insulin Delivery System Rating Questionnaire": translation, cross-cultural adaptation and validation
- PMID: 34033280
- PMCID: PMC10528609
- DOI: 10.20945/2359-3997000000274
Brazilian version of "The Insulin Delivery System Rating Questionnaire": translation, cross-cultural adaptation and validation
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to translate and cross-culturally adapt the Insulin Delivery System Rating Questionnaire (IDSRQ) for Brazilian users. Validation and reliability analysis of measures were also performed.
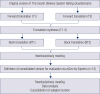
Methods: Methodological study comprising the following stages: forward translation, synthesis, back-translation, assessment by Expert Committee, pre-test and validation. International guidelines for translation and cross-cultural adaptation of measurement tools were followed. Validation data provided information about reliability (internal consistency, test-retest) and construct validity of the IDSRQ.
Results: Content validation by Experts' assessment was successful, with a mean Content Validity Index of 0.87 (±0.2). The IDSRQ validation study involved 113 T1DM patients, 46% male, mean age 32.61 (±12.59) years and mean age at diagnosis of diabetes of 17.51 (±12.41). The scale presented good internal consistency (Cronbach's alpha =0.786). The reliability analysis of the instrument was conducted by calculating the Intra-class Correlation Coefficient 0.885 (0.834-0.921), which indicated adequate concordance in all measures.
Conclusion: The translated and cross-culturally adapted Brazilian Portuguese version of the IDSRQ may be used to assess health-related quality of life (HRQOL) and treatment preferences for insulin delivery systems in T1DM Brazilian patients.
Keywords: Translation; cultural adaptation; diabetes mellitus; health related quality of life; insulin.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: no potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Bhatt JK, Thomas S, Nanjan MJ. Health Outcome Measures for Diabetes Mellitus: A Review. Appl Res Qual Life. 2012;7:413-43.
-
- Dickinson JK, Guzman SJ, Maryniuk MD, O’Brian CA, Kadohiro JK, Jackson RA, et al. The use of language in diabetes care and education. Diabetes Care. 2017;40(12):1790-9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources