Age-related changes in the local milieu of inflamed tissues cause aberrant neutrophil trafficking and subsequent remote organ damage
- PMID: 34033752
- PMCID: PMC8284598
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2021.04.025
Age-related changes in the local milieu of inflamed tissues cause aberrant neutrophil trafficking and subsequent remote organ damage
Abstract
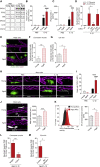
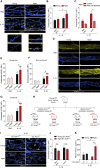
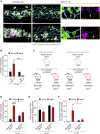
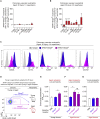
Aging is associated with dysregulated immune functions. Here, we investigated the impact of age on neutrophil diapedesis. Using confocal intravital microscopy, we found that in aged mice, neutrophils adhered to vascular endothelium in inflamed tissues but exhibited a high frequency of reverse transendothelial migration (rTEM). This retrograde breaching of the endothelium by neutrophils was governed by enhanced production of the chemokine CXCL1 from mast cells that localized at endothelial cell (EC) junctions. Increased EC expression of the atypical chemokine receptor 1 (ACKR1) supported this pro-inflammatory milieu in aged venules. Accumulation of CXCL1 caused desensitization of the chemokine receptor CXCR2 on neutrophils and loss of neutrophil directional motility within EC junctions. Fluorescent tracking revealed that in aged mice, neutrophils undergoing rTEM re-entered the circulation and disseminated to the lungs where they caused vascular leakage. Thus, neutrophils stemming from a local inflammatory site contribute to remote organ damage, with implication to the dysregulated systemic inflammation associated with aging.
Keywords: ACKR1; CXCR2; Neutrophils; aging; chemokines; diapedesis; endothelium; extravasation; inflammation; mast cells.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Comment in
-
Neutrophils hit reverse in ageing.Nat Rev Immunol. 2021 Jul;21(7):408-409. doi: 10.1038/s41577-021-00569-0. Nat Rev Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34079098 No abstract available.
-
Aged vasculature drives neutrophils mad.Immunity. 2021 Jul 13;54(7):1369-1371. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2021.06.010. Immunity. 2021. PMID: 34260883
References
-
- Akbar A.N., Gilroy D.W. Aging immunity may exacerbate COVID-19. Science. 2020;369:256–257. - PubMed
-
- Aragay A.M., Ruiz-Gómez A., Penela P., Sarnago S., Elorza A., Jiménez-Sainz M.C., Mayor F., Jr. G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 (GRK2): mechanisms of regulation and physiological functions. FEBS Lett. 1998;430:37–40. - PubMed
-
- Asai K., Kitaura J., Kawakami Y., Yamagata N., Tsai M., Carbone D.P., Liu F.T., Galli S.J., Kawakami T. Regulation of mast cell survival by IgE. Immunity. 2001;14:791–800. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

