Characterization of drug binding with alpha1-acid glycoprotein in clinical samples using ultrafast affinity extraction
- PMID: 34034105
- PMCID: PMC8186453
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chroma.2021.462240
Characterization of drug binding with alpha1-acid glycoprotein in clinical samples using ultrafast affinity extraction
Abstract
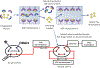
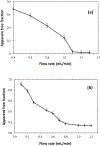
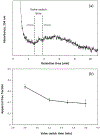
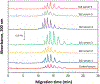
Many drugs bind to serum transport proteins, which can affect both drug distribution and activity in the body. α1-Acid glycoprotein (AGP) is a key transport protein for basic and neutral drugs. Both elevated levels and altered glycosylation patterns of AGP have been seen in clinical conditions such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). This study developed, optimized, and used the method of ultrafast affinity extraction (UAE) to examine whether these changes in AGP are associated with changes in the binding by some drugs to this transport protein. This approach used affinity microcolumns to capture and measure, in serum, the free fractions of several drugs known to bind AGP. These measurements were made with pooled normal control serum and serum samples from individuals with SLE. Immunoaffinity chromatography was used to obtain the content of AGP and HSA in these samples, and CE was used to examine the glycoform pattern for AGP in each serum sample. The free drug fractions measured for normal control serum ranged from 3.5 to 29.1%, in agreement with the results of ultrafiltration, and provided binding constants of ~105-106 M-1 for the given drugs with AGP at 37⁰C. Analysis of a screening set of SLE serum samples by UAE gave decreased free fractions (relative change, 12-55%) vs normal serum when spiked with the same types and amounts of drugs. These changes were related in some cases to AGP content, with some SLE samples having AGP levels 1.3- to 2.1-fold above the upper end of the normal range. In other cases, the changes in free fractions appeared to be linked to alterations in the glycoforms and binding constants of AGP, with some affinities differing by 1.2- to 1.5-fold vs normal AGP. This approach can be employed with other solute-protein systems and to investigate binding by other drugs or transport proteins directly in clinical samples.
Keywords: Alpha(1)-acid glycoprotein; Drug-protein binding; Human serum albumin; Systemic lupus erythematosus; Ultrafast affinity extraction.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose as related to this research.
Figures

References
-
- Fanali PAG, Fasano M, Pallottini V, Trezza V, Clinical relevance of drug binding to plasma proteins, J. Mol. Structure 1077 (2014) 4–13.
-
- Li Z, Beeram SR, Bi C, Suresh D, Zheng X, Hage DS, High-performance affinity chromatography: applications in drug-protein binding studies and personalized medicine, Adv. Protein Chem. Struct. Biol 102 (2016) 1–39. - PubMed
-
- Otagiri M, A molecular functional study on the interactions of drugs with plasma proteins, Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet 20 (2005) 309–323. - PubMed
-
- Schmidt S, Gonzalez D, Derendorf H, Significance of protein binding in pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics, J. Pharm. Sci 99 (2010) 1107–1122. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

