Anti-tumor effect of trametinib in bladder cancer organoid and the underlying mechanism
- PMID: 34034619
- PMCID: PMC8386751
- DOI: 10.1080/15384047.2021.1919004
Anti-tumor effect of trametinib in bladder cancer organoid and the underlying mechanism
Abstract
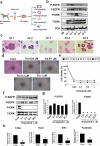
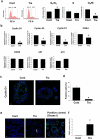
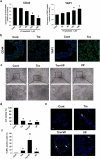
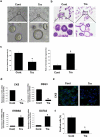
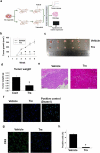
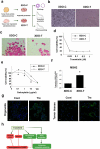
Bladder cancer (BC), a main neoplasm of urinary tract, is usually inoperable and unresponsive to chemotherapy. As a novel experimental model for muscle-invasive BC, we previously established a culture method of dog BC organoids. In the present study, the detailed in vitro and in vivo anti-tumor effects of trametinib were investigated by using this model. In each BC organoid strain, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)/ERK signaling was upregulated compared with normal bladder cells. Trametinib even at a low concentration inhibited the cell viability of BC organoids and the activation of ERK through decreasing expression of c-Myc, ELK1, SIK1, and PLA2G4A. Trametinib arrested cell cycle of BC with few apoptosis. Dual treatment of BC organoids with trametinib and YAP inhibitor, verteporfin extremely inhibited the cell viability with apoptosis induction. Moreover, trametinib induced basal to luminal differentiation of BC organoids by upregulating luminal markers and downregulating basal ones. In vivo, trametinib decreased the tumor growth of BC organoids in mice and the xenograft-derived organoids from trametinib-administered mice showed enhanced sensitivity to carboplatin due to MSH2 upregulation. Our data suggested a new strategy of trametinib-YAP inhibitor or trametinib-carboplatin combination as a promising treatment of BC.
Keywords: Muscle-invasive bladder cancer; combination therapy; dog; organoid; trametinib.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lerner SP, Schoenberg M, Sternberg C. 2006. Textbook of bladder cancer. Oxon. UK: Taylor and Francis. doi:10.1201/9780367800130 - DOI
-
- Elbadawy M, Usui T, Mori T, Tsunedomi R, Hazama S, Nabeta R, Uchide T, Fukushima R, Yoshida T, Shibutani M, et al. Establishment of a novel experimental model for muscle-invasive bladder cancer using a dog bladder cancer organoid culture. Cancer Sci. 2019;110(9):2806–2821. doi:10.1111/cas.14118. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
