Therapeutic effect of various ginsenosides on rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 34034706
- PMCID: PMC8145820
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-021-03302-5
Therapeutic effect of various ginsenosides on rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Background: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease which causes disability and threatens the health of humans. Therefore, it is of great significance to seek novel effective drugs for RA. It has been reported that various ginsenoside monomers are able to treat RA. However, it is still unclear which ginsenoside is the most effective and has the potential to be developed into an anti-RA drug.
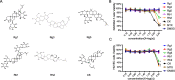
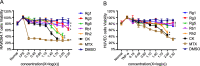
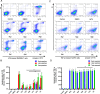
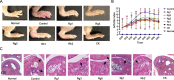
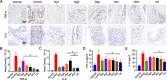
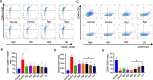
Methods: The ginsenosides, including Rg1, Rg3, Rg5, Rb1, Rh2 and CK, were evaluated and compared for their therapeutic effect on RA. In in vitro cell studies, methotrexate (MTX) and 0.05% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) was set as a positive control group and a negative control group, respectively. LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells and TNF-α-induced HUVEC cells were cultured with MTX, DMSO and six ginsenosides, respectively. Cell proliferation was analyzed by MTT assay and cell apoptosis was carried out by flow cytometry. CIA mice model was developed to evaluate the therapeutic efficacy of ginsenosides. The analysis of histology, immunohistochemistry, flow cytometry and cytokine detections of the joint tissues were performed to elucidate the action mechanisms of ginsenosides.
Results: All six ginsenosides showed good therapeutic effect on acute arthritis compared with the negative control group, Ginsenoside CK provided the most effective treatment ability. It could significantly inhibit the proliferation and promote the apoptosis of RAW 264.7 and HUVEC cells, and substantially reduce the swelling, redness, functional impairment of joints and the pathological changes of CIA mice. Meanwhile, CK could increase CD8 + T cell to down-regulate the immune response, decrease the number of activated CD4 + T cell and proinflammatory M1-macrophages, thus resulting in the inhibition of the secretion of proinflammatory cytokine such as TNF-α and IL-6.
Conclusion: Ginsenoside CK was proved to be a most potential candidate among the tested ginsenosides for the treatment of RA, with a strong anti-inflammation and immune modulating capabilities.
Keywords: CIA; Ginsenoside compound K; Panax ginseng; Rheumatoid arthritis; Therapeutic effect.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest with any parties or individuals.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Neuroprotective Effects of Ginsenosides against Cerebral Ischemia.Molecules. 2019 Mar 20;24(6):1102. doi: 10.3390/molecules24061102. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 30897756 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-arthritic effect of ginsenoside Rb1 on collagen induced arthritis in mice.Int Immunopharmacol. 2007 Oct;7(10):1286-91. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2007.05.006. Epub 2007 Jun 26. Int Immunopharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17673143
-
Ginsenoside Rc from Korean Red Ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer) Attenuates Inflammatory Symptoms of Gastritis, Hepatitis and Arthritis.Am J Chin Med. 2016;44(3):595-615. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X16500336. Epub 2016 Apr 24. Am J Chin Med. 2016. PMID: 27109153
-
Ginsenoside compound K- a potential drug for rheumatoid arthritis.Pharmacol Res. 2021 Apr;166:105498. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105498. Epub 2021 Feb 17. Pharmacol Res. 2021. PMID: 33609698 Review.
-
Pro-Resolving Effect of Ginsenosides as an Anti-Inflammatory Mechanism of Panax ginseng.Biomolecules. 2020 Mar 13;10(3):444. doi: 10.3390/biom10030444. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32183094 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Isolation of oligostilbenes from Iris lactea Pall. var. chinensis (Fisch.) Koidz and their anti-inflammatory activities.RSC Adv. 2022 Nov 16;12(51):32912-32922. doi: 10.1039/d2ra05176a. eCollection 2022 Nov 15. RSC Adv. 2022. PMID: 36425180 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Characters and Pharmacological Activity of Protopanaxadiol-Type Saponins and Protopanaxatriol-Type Saponins from Ginseng.Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci. 2024 Jun 24;2024:9096774. doi: 10.1155/2024/9096774. eCollection 2024. Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci. 2024. PMID: 38957183 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of Key Chemical Components in Aqueous Extract Sediments of Panax Ginseng at Different Ages.Foods. 2022 Apr 16;11(8):1161. doi: 10.3390/foods11081161. Foods. 2022. PMID: 35454749 Free PMC article.
-
Triterpenes as Potential Drug Candidates for Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment.Life (Basel). 2023 Jul 5;13(7):1514. doi: 10.3390/life13071514. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37511889 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ninjin'yoeito suppressed the onset of arthritis, pain, and muscle atrophy in rheumatoid arthritis model mice.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Dec 19;13:974380. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.974380. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36601050 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

