MicroRNA-1: Diverse role of a small player in multiple cancers
- PMID: 34034986
- PMCID: PMC8606619
- DOI: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2021.05.020
MicroRNA-1: Diverse role of a small player in multiple cancers
Abstract
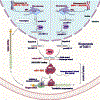
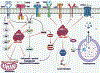
The process of cancer initiation and development is a dynamic and complex mechanism involving multiple genetic and non-genetic variations. With the development of high throughput techniques like next-generation sequencing, the field of cancer biology extended beyond the protein-coding genes. It brought the functional role of noncoding RNAs into cancer-associated pathways. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are one such class of noncoding RNAs regulating different cancer development aspects, including progression and metastasis. MicroRNA-1 (miR-1) is a highly conserved miRNA with a functional role in developing skeletal muscle precursor cells and cardiomyocytes and acts as a consistent tumor suppressor gene. In humans, two discrete genes, MIR-1-1 located on 20q13.333 and MIR-1-2 located on 18q11.2 loci encode for a single mature miR-1. Downregulation of miR-1 has been demonstrated in multiple cancers, including lung, breast, liver, prostate, colorectal, pancreatic, medulloblastoma, and gastric cancer. A vast number of studies have shown that miR-1 affects the hallmarks of cancer like proliferation, invasion and metastasis, apoptosis, angiogenesis, chemosensitization, and immune modulation. The potential therapeutic applications of miR-1 in multiple cancer pathways provide a novel platform for developing anticancer therapies. This review focuses on the different antitumorigenic and therapeutic aspects of miR-1, including how it regulates tumor development and associated immunomodulatory functions.
Keywords: Cancer therapeutics; Chemosensitivity; Immunoregulation; MiR-1; MiRNAs.
Copyright © 2021. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement
SKB is co-founder of Sanguine Diagnostics and Therapeutics, Inc. Other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dysregulated expression and functions of microRNA-330 in cancers: A potential therapeutic target.Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Feb;146:112600. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112600. Epub 2021 Dec 27. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 34968919
-
The microRNA expression signature of bladder cancer by deep sequencing: the functional significance of the miR-195/497 cluster.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 10;9(2):e84311. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084311. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24520312 Free PMC article.
-
Promising therapeutic role of miR-27b in tumor.Tumour Biol. 2017 Mar;39(3):1010428317691657. doi: 10.1177/1010428317691657. Tumour Biol. 2017. PMID: 28351320 Review.
-
MicroRNA-212 negatively regulates starvation induced autophagy in prostate cancer cells by inhibiting SIRT1 and is a modulator of angiogenesis and cellular senescence.Oncotarget. 2015 Oct 27;6(33):34446-57. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5920. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26439987 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA and cancer; computational and experimental approaches.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2014;15(5):429. doi: 10.2174/138920101505140828161335. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 25189575
Cited by
-
Screening and identification of miRNAs negatively regulating FAM83A/Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 29;14(1):17394. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-67686-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39075121 Free PMC article.
-
Helicobacter pylori promotes gastric cancer through CagA-mediated mitochondrial cholesterol accumulation by targeting CYP11A1 redistribution.Int J Biol Sci. 2024 Jul 15;20(10):4007-4028. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.96425. eCollection 2024. Int J Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39113698 Free PMC article.
-
Electroacupuncture ameliorates AOM/DSS-induced mice colorectal cancer by inhibiting inflammation and promoting autophagy via the SIRT1/miR-215/Atg14 axis.Aging (Albany NY). 2023 Nov 22;15(22):13194-13212. doi: 10.18632/aging.205236. Epub 2023 Nov 22. Aging (Albany NY). 2023. PMID: 38006398 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA-1 promotes acute myeloid leukemia cell pathogenesis through metabolic regulation.Front Genet. 2023 May 9;14:1192799. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1192799. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 37229187 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-1 attenuates the growth and metastasis of small cell lung cancer through CXCR4/FOXM1/RRM2 axis.Mol Cancer. 2023 Jan 4;22(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01695-6. Mol Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36597126 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

