Complement control for COVID-19
- PMID: 34035117
- PMCID: PMC8432947
- DOI: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abj1014
Complement control for COVID-19
Abstract
Excessive complement activation contributes to lung disease and adverse patient outcomes in COVID-19 (see the related Research Articles by Yan et al and Ma et al).
Copyright © 2021, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Figures
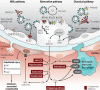
Comment on
-
SARS-CoV-2 drives JAK1/2-dependent local complement hyperactivation.Sci Immunol. 2021 Apr 7;6(58):eabg0833. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abg0833. Sci Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33827897 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ma L., Sahu S. K., Cano M., Kuppuswamy V., Bajwa J., McPhatter J., Pine A., Meizlish M. L., Goshua G., Chang C.-H., Zhang H., Price C., Bahel P., Rinder H., Lei T., Day A., Reynolds D., Wu X., Schriefer R., Rauseo A. M., Goss C. W., O’Halloran J. A., Presti R. M., Kim A. H., Gelman A. E., Dela Cruz C. S., Lee A. I., Mudd P. A., Chun H. J., Atkinson J. P., Kulkarni H. S., Increased complement activation is a distinctive feature of severe SARS-CoV-2 infection. Sci. Immunol. 6, eabh2259 (2021). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Huang J., Hume A. J., Abo K. M., Werder R. B., Villacorta-Martin C., Alysandratos K. D., Beermann M. L., Simone-Roach C., Lindstrom-Vautrin J., Olejnik J., Suder E. L., Bullitt E., Hinds A., Sharma A., Bosmann M., Wang R., Hawkins F., Burks E. J., Saeed M., Wilson A. A., Mühlberger E., Kotton D. N., SARS-CoV-2 infection of pluripotent stem cell-derived human lung alveolar type 2 cells elicits a rapid epithelial-intrinsic inflammatory response. Cell Stem Cell 27, 962–973.e7 (2020). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Huber-Lang M., Sarma J. V., Zetoune F. S., Rittirsch D., Neff T. A., McGuire S. R., Lambris J. D., Warner R. L., Flierl M. A., Hoesel L. M., Gebhard F., Younger J. G., Drouin S. M., Wetsel R. A., Ward P. A., Generation of C5a in the absence of C3: A new complement activation pathway. Nat. Med. 12, 682–687 (2006). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

