Upregulation of wild-type p53 by small molecule-induced elevation of NQO1 in non-small cell lung cancer cells
- PMID: 34035487
- PMCID: PMC8888561
- DOI: 10.1038/s41401-021-00691-8
Upregulation of wild-type p53 by small molecule-induced elevation of NQO1 in non-small cell lung cancer cells
Abstract
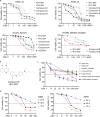
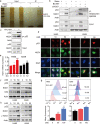
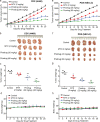
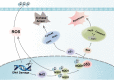
The tumor suppressor p53 is usually inactivated by somatic mutations in malignant neoplasms, and its reactivation represents an attractive therapeutic strategy for cancers. Here, we reported that a new quinolone compound RYL-687 significantly inhibited non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells which express wild type (wt) p53, in contract to its much weaker cytotoxicity on cells with mutant p53. RYL-687 upregulated p53 in cells with wt but not mutant p53, and ectopic expression of wt p53 significantly enhanced the anti-NSCLC activity of this compound. RYL-687 induced production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and upregulation of Nrf2, leading to an elevation of the NAD(P)H:quinoneoxidoreductase-1 (NQO1) that can protect p53 by inhibiting its degradation by 20S proteasome. RYL-687 bound NQO1, facilitating the physical interaction between NQO1 and p53. NQO1 was required for RYL-687-induced p53 accumulation, because silencing of NQO1 by specific siRNA or an NQO1 inhibitor uridine, drastically suppressed RYL-687-induced p53 upregulation. Moreover, a RYL-687-related prodrug significantly inhibited tumor growth in NOD-SCID mice inoculated with NSCLC cells and in a wt p53-NSCLC patient-derived xenograft mouse model. These data indicate that targeting NQO1 is a rational strategy to reactivate p53, and RYL-687 as a p53 stabilizer bears therapeutic potentials in NSCLCs with wt p53.
Keywords: NQO1; RYL-687; non-small cell lung cancer; p53.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to CPS and SIMM.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Herbst RS, Morgensztern D, Boshoff C. The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature. 2018;553:446–54. - PubMed
-
- Hirsch FR, Scagliotti GV, Mulshine JL, Kwon R, Curran WJ, Jr., Wu YL, et al. Lung cancer: current therapies and new targeted treatments. Lancet. 2017;389:299–311. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69:7–34. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

