Maternal Near Miss: Unraveling Our Experience in the Tertiary Care Hospital of Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- PMID: 34035573
- PMCID: PMC8117887
- DOI: 10.4103/ijcm.IJCM_145_20
Maternal Near Miss: Unraveling Our Experience in the Tertiary Care Hospital of Andaman and Nicobar Islands
Abstract
Context: Women who survive life-threatening complications related to pregnancy and delivery have many common aspects with those who die of such complications. This similarity brought forward the near miss concept in maternal health. Analysis of the similarities, differences, and the relationship between these two groups of women provide a complete assessment of quality of maternal health care.
Aims: The aim of this study is to assess the baseline indices of maternal near miss (MNM) and analyze the quality of care at a tertiary care center in Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Settings and design: Facility-based, cross-sectional study.
Subjects and methods: The study was conducted for a period of 18 months from January 1, 2015, to August 31, 2016. Cases, who met the World Health Organization (WHO) criteria of severe obstetric morbidity, were included and followed up during their hospital stay and till their discharge or death. Quality of maternal health care was assessed through the WHO near-miss criteria and criterion-based clinical audit methodology.
Statistical analysis used: Descriptive statistics using mean and percentages and Student's t-test were used.
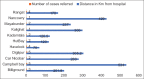
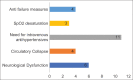
Results: Among 4720 women who delivered in our hospital, there were 4677 live births, 52 patients were near miss, and there were 9 maternal deaths. The MNM incidence ratio was 11.11%, the MNM mortality ratio was 5.77, and the mortality index 14.75%. The most common cause of maternal morbidity was hemorrhage followed by hypertensive disorders.
Conclusions: Improving referral systems, effective use of critical care, and evidence-based interventions can potentially reduce severe maternal outcomes.
Keywords: Intensive care unit; maternal near miss; morbidity; mortality index.
Copyright: © 2021 Indian Journal of Community Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Maternal near-miss and mortality associated with hypertensive disorders of pregnancy remote from term: a multicenter observational study in Ghana.AJOG Glob Rep. 2022 Jan 12;2(2):100045. doi: 10.1016/j.xagr.2021.100045. eCollection 2022 May. AJOG Glob Rep. 2022. PMID: 36275498 Free PMC article.
-
Incidence of maternal near miss in the public health sector of Harare, Zimbabwe: a prospective descriptive study.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2018 Nov 26;18(1):458. doi: 10.1186/s12884-018-2092-7. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2018. PMID: 30477449 Free PMC article.
-
Incidence of Maternal "Near-Miss" Events in a Tertiary Care Hospital of Central Gujarat, India.J Obstet Gynaecol India. 2016 Oct;66(Suppl 1):315-20. doi: 10.1007/s13224-016-0901-3. Epub 2016 Jun 13. J Obstet Gynaecol India. 2016. PMID: 27651623 Free PMC article.
-
Every maternal near-miss counts: Need for a national audit in South Africa? A mixed-methods study.S Afr Med J. 2022 Aug 30;112(9):769-777. doi: 10.7196/SAMJ.2022.v112.i9.16248. S Afr Med J. 2022. PMID: 36214035
-
Maternal near miss events in India.Indian J Med Res. 2021 Apr;154(4):573-582. doi: 10.4103/ijmr.IJMR_928_19. Indian J Med Res. 2021. PMID: 35435342 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Say L, Souza JP, Pattinson RC WHO Working Group on Maternal Mortality and Morbidity Classifications. Maternal near miss-towards a standard tool for monitoring quality of maternal health care. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2009;23:287–96. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Evaluating the Quality of Care for Severe Pregnancy Complication: The WHO Near Miss Approach for Maternal Health. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2011. [Last accessed on 2020 Aug 18]. Available from: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/44692/9789241502221_eng... .
-
- Government of India, NITI Aayog Report. URL. [Last accessed on 2019 May 2019]. Available from: https://niti.gov.in/content/maternal-mortality-ratio-mmr-100000-livebirths .
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous