Enamel Surface Damage following Debonding of Ceramic Brackets: A Hospital-Based Study
- PMID: 34035672
- PMCID: PMC8124004
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/5561040
Enamel Surface Damage following Debonding of Ceramic Brackets: A Hospital-Based Study
Abstract
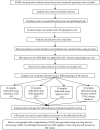
Methods: The current study includes 80 extracted premolars of human from the patient visiting for orthodontic treatment of Coorg Institute of Dental Sciences, Karnataka, India. The brackets were debonded using four different methods. The enamel surface damage after the procedure was assessed with the Enamel Surface Index (ESI); similarly, the Adhesive Remnant Index (ARI) score was used to determine the adhesive residual deposit. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was used to visualize better microporosities and micromechanical retention of adhesive remnants on the enamel surface. The normality of the data was tested using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. Depending upon the normality test result, the one-way ANOVA test or Kruskal-Wallis test was used to test the mean ESI and mean ARI differences among different debonding methods along with the appropriate post hoc tests. The necessary ethical clearance was obtained from the Ethics Committee of the institute.
Results: The ultrasonic scaler (US) technique led to more significant enamel surface damage, with 13 (65%) samples in the ESI scores III and IV against the satisfactory surface in 2 (10%) samples with the ligature cutter (LC) technique (ESI-I) reflecting LC as a better technique. The ESI scores (III and IV) for debonding plier (DP) and thermal method (TM) reflected a higher value in 12 (60%) and 10 (50%) samples and caused more damage to the enamel surface as compared to the LC technique. The ARI score was highest (ARI-1 = 40%) with the LC technique, followed by the US (ARI-1 = 20%), TM (ARI-1 = 15%), and DP (ARI-1 = 5%) methods. We have observed a significant association (p value <0.05) of the ARI score among four different debonding ways in terms of each tooth's residual adhesive after the bracket removal.
Conclusion: The result establishes the LC technique as a more acceptable one as it causes minimal harm to the debonded surface. The adhesive left on the debonded area is also minimum as compared to the other three methods tested. Therefore, it can be suggested as an ideal method.
Copyright © 2021 Neelutpal Bora et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Comparative Evaluation of Enamel Microfracture and Adhesive Remnant Index of Adhesive Precoated Flash-free System vs Conventional Bonding Using Different Debonding Techniques: An In Vitro Study.J Contemp Dent Pract. 2025 Apr 1;26(4):388-396. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-3858. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2025. PMID: 40583429
-
Er:YAG Laser for Metal and Ceramic Bracket Debonding: An In Vitro Study on Intrapulpal Temperature, SEM, and EDS Analysis.Photomed Laser Surg. 2018 Nov;36(11):595-600. doi: 10.1089/pho.2017.4412. Epub 2018 Jun 15. Photomed Laser Surg. 2018. PMID: 29905504
-
Loss of surface enamel after bracket debonding: an in-vivo and ex-vivo evaluation.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2010 Oct;138(4):387.e1-387.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2010.01.028. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2010. PMID: 20889035
-
Effect of varying etching times on the bond strength of ceramic brackets.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1996 Apr;109(4):403-9. doi: 10.1016/s0889-5406(96)70122-1. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1996. PMID: 8638582 Review.
-
What is the safest method of orthodontic debonding - a systematic review of the literature.Folia Med Cracov. 2023 Oct 30;63(3):133-156. doi: 10.24425/fmc.2023.147219. Folia Med Cracov. 2023. PMID: 38310534
Cited by
-
Morphological Characteristics and Prevention of Tooth Enamel Demineralization during Orthodontic Treatment with Non-Removable Appliances.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Dec 29;20(1):540. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20010540. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36612862 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of Thermocycling with Two Different Curing Techniques on Enamel Micro-Cracks Formation, Debonding, and Failure Modes of Ceramic Brackets: An In Vitro Study.Materials (Basel). 2024 Jul 31;17(15):3765. doi: 10.3390/ma17153765. Materials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39124430 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of enamel surface roughness and hardness with metal and ceramic orthodontic brackets using different etching and adhesive systems: An in vitro study.Saudi Dent J. 2023 Sep;35(6):641-650. doi: 10.1016/j.sdentj.2023.05.015. Epub 2023 May 24. Saudi Dent J. 2023. PMID: 37817787 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

