Current Management of Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease
- PMID: 34035691
- PMCID: PMC8132623
Current Management of Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease
Abstract
Alcohol consumption is a major risk factor for various diseases worldwide and is one of the most common causes of chronic liver disease. Alcohol use has risen over the past 30 years and is forecast to continue to rise. Concurrently, there has been an increased incidence of alcohol-associated liver disease (ALD). Alcohol use, regardless of the amount, leads to years of health loss across populations when considering the strong association between alcohol consumption and overall disease burden. Given the rising incidence of ALD and associated mortality, it is imperative to study the underlying factors driving these trends. This article summarizes the diagnosis and management of ALD, with a focus on various screening and prognostic tools and treatments for alcohol-associated hepatitis.
Keywords: Alcohol-associated liver disease; alcohol-associated hepatitis; alcoholic cirrhosis; alcoholic hepatitis; cirrhosis; liver transplantation.
Copyright © 2020, Gastro-Hep Communications, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose.
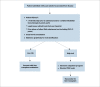
Figures
References
-
- Manthey J, Shield KD, Rylett M, Hasan OSM, Probst C, Rehm J. Global alcohol exposure between 1990 and 2017 and forecasts until 2030: a modelling study. Lancet. 2019;393(10190):2493–2502. - PubMed
-
- Goldberg D, Ditah IC, Saeian K et al. Changes in the prevalence of hepatitis C virus infection, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, and alcoholic liver disease among patients with cirrhosis or liver failure on the waitlist for liver transplantation. Gastroenterology. 2017;152(5):1090–1099.e1. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
