Predicting potential future reduction in shark bites on people
- PMID: 34035935
- PMCID: PMC8101541
- DOI: 10.1098/rsos.201197
Predicting potential future reduction in shark bites on people
Abstract
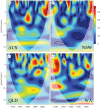
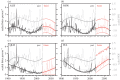
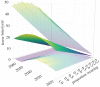
Despite the low chance of a person being bitten by a shark, there are serious associated costs. Electronic deterrents are currently the only types of personal deterrent with empirical evidence of a substantial reduction in the probability of being bitten by a shark. We aimed to predict the number of people who could potentially avoid being bitten by sharks in Australia if they wear personal electronic deterrents. We used the Australian Shark Attack File from 1900 to 2020 to develop sinusoidal time-series models of per capita incidents, and then stochastically projected these to 2066. We predicted that up to 1063 people (range: 185-2118) could potentially avoid being bitten across Australia by 2066 if all people used the devices. Avoiding death and injury of people over the next half-century is of course highly desirable, especially when considering the additional costs associated with the loss of recreational, commercial and tourism revenue potentially in the tens to hundreds of millions of dollars following clusters of shark-bite events.
Keywords: bull shark; shark attack; shark–human interactions; tiger shark; white shark.
© 2021 The Authors.
Figures

References
-
- McPhee D. 2014. Unprovoked shark bites: are they becoming more prevalent? Coastal Manage. 42, 478-492. ( 10.1080/08920753.2014.942046) - DOI
-
- Ferretti F, Jorgensen S, Chapple TK, De Leo G, Micheli F.. 2015. Reconciling predator conservation with public safety. Front. Ecol. Environ. 13, 412-417. ( 10.1890/150109) - DOI
-
- Ryan LA, Lynch SK, Harcourt R, Slip DJ, Peddemors V, Everett JD, Harrison LM, Hart NS. 2019. Environmental predictive models for shark attacks in Australian waters. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 631, 165-179. ( 10.3354/meps13138) - DOI
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
