Ulcerative Colitis With Concomitant Serrated Polyposis Syndrome: A Case Report and Literature Review
- PMID: 34036009
- PMCID: PMC8136465
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.14591
Ulcerative Colitis With Concomitant Serrated Polyposis Syndrome: A Case Report and Literature Review
Abstract
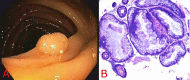
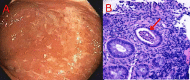
Serrated polyposis syndrome (SPS) is a pre-cancerous condition associated with increased risk of developing colorectal cancer (CRC). Its role in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)-associated CRC remains unknown. Despite the growing understanding and recognition of SPS, there is limited literature about its impact on the colon in individuals with IBD. Herein, we report a case of a 45-year-old female who was diagnosed with ulcerative colitis (UC) and SPS. We also reviewed the literature surrounding this association and highlighted the intricacies in managing this unique patient population. At present, there are no screening guidelines for CRC in SPS patients with IBD. However, given the potential synergistic risk for CRC, a close surveillance approach may be utilized. Tracking lifetime cumulative features of SPS and endoscopic clearance of adenomas and serrated polyps are the mainstays of management.
Keywords: colorectal cancer (crc); inflammatory bowel disease; serrated polyp; serrated polyposis syndrome (sps); sessile serrated adenoma; ulcerative colitis (uc).
Copyright © 2021, Mansour et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Cancer risk in inflammatory bowel disease: a 6-year prospective multicenter nested case-control IG-IBD study. Biancone L, Armuzzi A, Scribano ML, et al. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2020;26:450–459. - PubMed
-
- European consensus on the histopathology of inflammatory bowel disease. Magro F, Langner C, Driessen A, et al. J Crohns Colitis. 2013;7:827–851. - PubMed
-
- Gastrointestinal pathology. Mod Pathol. 2017;30:157–210. - PubMed
-
- Hyperplastic polyposis of the colon and rectum. Renaut AJ, Douglas PR, Newstead GL. Colorectal Dis. 2002;4:213–215. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
