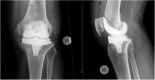
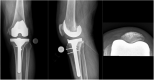
Late prosthetic knee joint infection with Staphylococcus xylosus
- PMID: 34036044
- PMCID: PMC8138718
- DOI: 10.1016/j.idcr.2021.e01160
Late prosthetic knee joint infection with Staphylococcus xylosus
Abstract
Prosthethic Joint Infection (PJI) is a severe complication following joint replacement. Late PJI can occur years after implantation by hematogenous seeding of a microbial agent. Staphylococcus xylosus is a coagulase-negative commensal of the human skin and rarely associated with opportunistic human infections. We report the rare case of a 70-year old Patient suffering from knee pain 18 years after primary Total Knee Arthroplasty. Microbiological sampling detected S. xylosus as causative agent. The patient was successfully treated with a two-stage implant exchange and antibiotic therapy using co-amoxicillin and rifampicin/cotrimoxazol. This case illustrates the ability of S. xylosus to cause late PJI and the importance of not letting coagulase-negative Staphylococci be routinely categorized as contaminants of microbiological samples.
Keywords: PJI; Prosthetic joint infection; Staphylococcus xylosus; TKA; Total knee arthroplasty.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Different microbiological profiles between hip and knee prosthetic joint infections.J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2019 May-Aug;27(2):2309499019847768. doi: 10.1177/2309499019847768. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2019. PMID: 31117922
-
Microbiological pattern of prosthetic hip and knee infections: a high-volume, single-centre experience in China.J Med Microbiol. 2021 Mar;70(3). doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.001305. Epub 2021 Jan 15. J Med Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33448922
-
Prior hip or knee prosthetic joint infection in another joint increases risk three-fold of prosthetic joint infection after primary total knee arthroplasty: a matched control study.Bone Joint J. 2019 Jul;101-B(7_Supple_C):91-97. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.101B7.BJJ-2018-1189.R1. Bone Joint J. 2019. PMID: 31256641
-
[Comparison of therapeutic strategies for hip and knee prosthetic joint infection].Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2009 Aug;76(4):302-9. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2009. PMID: 19755054 Review. Czech.
-
Sonication contribution to identifying prosthetic joint infection with Ralstonia pickettii: a case report and review of the literature.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017 Jul 19;18(1):311. doi: 10.1186/s12891-017-1678-y. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017. PMID: 28724376 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gabapentin-Induced Adrenal Insufficiency: The Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis Stress Misresponse and Risk of Infection: A Case Report and Literature Review.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Sep 5;17(9):1174. doi: 10.3390/ph17091174. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39338336 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The metagenomic and whole-genome metagenomic detection of multidrug-resistant bacteria from subclinical mastitis-affected cow's milk in India.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Apr 22;15:1549523. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1549523. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40330015 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of microbial communities in different growth stages of Dermacentor nuttalli.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Oct 14;9:1021426. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.1021426. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 36311671 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic exploration of the fermented meat isolate Staphylococcus shinii IMDO-S216 with a focus on competitiveness-enhancing secondary metabolites.BMC Genomics. 2024 Jun 7;25(1):575. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10490-0. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38849728 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schleifer K.H., Kloos W.E. Isolation and characterization of Staphylococci from human skin I. Amended descriptions of Staphylococcus epidermidis and Staphylococcus saprophyticus and descriptions of three new species: Staphylococcus cohnii, Staphylococcus haemolyticus, and Staphylococcus xylosus. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 1975;25(1):50–61.
-
- Conrad S.A., West B.C. Endocarditis caused by Staphylococcus xylosus associated with intravenous drug abuse. J Infect Dis. 1984;149(5):826–827. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources