Gastro protecting influence of Topiramate in ethanol produced gastric ulcers in rats
- PMID: 34036049
- PMCID: PMC8138487
- DOI: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2021.05.004
Gastro protecting influence of Topiramate in ethanol produced gastric ulcers in rats
Abstract
Background: Topiramate (TPM), an antiepileptic drug, is also effective against alcohol dependency, a crucial factor in forming gastric ulcers. There is an increased possibility of patients with compromised gastric conditions getting exposed to TPM, but its effect on gastric ulcers is unknown. This study investigates the implication of acute TPM in ethanol-produced gastric ulceration in rats.
Material and methods: The effect of TPM studied in male 200-225 g Sprague Dawley rats against ethanol-induced gastric ulcers and for gastric secretion and acidity. The factors assessed include gastric secretion and acidity, gastric ulcer score, biochemical and histological changes, NF-kB, and p53 expression. The analysis of data performed by using the Kruskal Wallis test and Dunnett's multiple comparison tests.
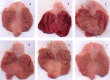
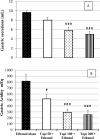
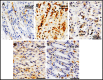
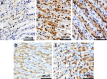
Results: TPM pretreatment showed gastroprotective effects. It significantly reduced ethanol-induced increased gastric secretion, acidity, and gastric ulcer index and prevented gastric mucus depletion. The ethanol-induced inflammation and apoptosis were also significantly decreased by reducing the increased gastric myeloperoxidase activity and the expression of NF-kB and p53. TPM pretreatment also reduced the ethanol-induced damage to the gastric histology in rats.
Conclusion: TPM exerted a gastro-protective effect against ethanol-induced gastric ulcers mediated by reducing the gastric ulcer index, preventing a decrease of the mucus levels, reduction in inflammation, damage to gastric histology, and a decrease in the enhanced expression of NF-kB and TPM. Further detailed investigations are essential to understand the chronic influence of TPM on gastric ulcers.
Keywords: Ethanol; Gastric ulcer; Myeloperoxidase; NF-kB; Rat; Topiramate; p5.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Azhari H., Underwood F., King J. A36. The global incidence of peptic ulcer disease and its complications at the turn of the 21st century: a systematic review. J. Can. Assoc. Gastroenterol. 2018;1(suppl_2):61–62. doi: 10.1093/jcag/gwy009.036. - DOI
-
- Tayeby F., Salman A.A.A., Kamran S., Khaing S.L., Salehen N.B., Mohan G.M.A.D. Ulcer prevention effect of 3, 4, 5-tihydroxy-n0-[(2-methyl-1h-indol-3yl) methylidene] benzo hydrazide in Hcl/ethanol-induced gastric mucosal damage in rats. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2017;14:1317–1326. doi: 10.7150/ijms.20984. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

