Long-range interaction effects on coupled excitable nodes: traveling waves and chimera state
- PMID: 34036198
- PMCID: PMC8134981
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e07026
Long-range interaction effects on coupled excitable nodes: traveling waves and chimera state
Abstract
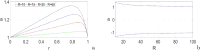
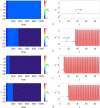
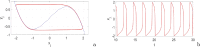
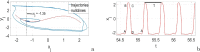
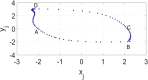
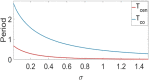
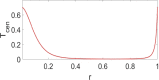
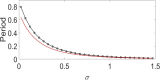
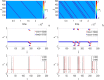
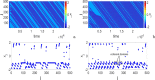
In this paper, analytical and numerical studies of the influence of the long-range interaction parameter on the excitability threshold in a ring of FitzHugh-Nagumo (FHN) system are investigated. The long-range interaction is introduced to the network to model regulation of the Gap junctions or hemichannels activity at the connexins level, which provides links between pre-synaptic and post-synaptic neurons. Results show that the long-range coupling enhances the range of the threshold parameter. We also investigate the long-range effects on the network dynamics, which induces enlargement of the oscillatory zone before the excitable regime. When considering bidirectional coupling, the long-range interaction induces traveling patterns such as traveling waves, while when considering unidirectional coupling, the long-range interaction induces multi-chimera states. We also studied the difference between the dynamics of coupled oscillators and coupled excitable neurons. We found that, for the coupled system, the oscillation period decreases with the increasing of the coupling parameter. For the same values of the coupling parameter, the oscillation period of the Oscillatory dynamics is greater than the oscillation period of the excitable dynamics. The analytical approximation shows good agreement with the numerical results.
Keywords: Electrical synapse; Excitable behavior; Long-range interaction; Multi-chimera state; Traveling waves.
© 2021 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

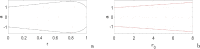



Similar articles
-
Controlling chimera states: The influence of excitable units.Phys Rev E. 2016 Feb;93(2):022217. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.93.022217. Epub 2016 Feb 25. Phys Rev E. 2016. PMID: 26986341
-
Role of coupling delay in oscillatory activity in autonomous networks of excitable neurons with dissipation.Chaos. 2023 Jul 1;33(7):073114. doi: 10.1063/5.0147883. Chaos. 2023. PMID: 37408151
-
Traveling waves in an ensemble of excitable oscillators: The interplay of memristive coupling and noise.Chaos. 2024 Dec 1;34(12):123110. doi: 10.1063/5.0215152. Chaos. 2024. PMID: 39621464
-
Chimera dynamics in an array of coupled FitzHugh-Nagumo system with shift of close neighbors.Heliyon. 2020 Apr 6;6(4):e03739. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e03739. eCollection 2020 Apr. Heliyon. 2020. PMID: 32280805 Free PMC article.
-
How to make a static cytokinetic furrow out of traveling excitable waves.Small GTPases. 2016 Apr 2;7(2):65-70. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2016.1168505. Epub 2016 Apr 12. Small GTPases. 2016. PMID: 27070950 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sàez J.C., Berthoud V.M., Branes M.C., Martinez A.D., Beyer E.C. Plasma membrane channels formed by connexins: their regulation and functions. Physiol. Rev. 2003;83:1359–1400. - PubMed
-
- Bean B.P. The action potential in mammalian central neurons. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007;8:451–465. - PubMed
-
- Vinken M., Vanhaecke T., Papeleu P., Snykers S., Henkens T., Rogiers V. Connexins and their channels in cell growth and cell death. Cell. Signal. 2006;18:592–600. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

