Tumor-Infiltrating Leukocyte Phenotypes Distinguish Outcomes in Related Patients With Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 34036232
- PMCID: PMC8140804
- DOI: 10.1200/PO.20.00287
Tumor-Infiltrating Leukocyte Phenotypes Distinguish Outcomes in Related Patients With Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO’s conflict of interest policy, please refer to www.asco.org/rwc or ascopubs.org/cci/author-center. Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (Open Payments). Carl R. PelzConsulting or Advisory Role, Immediate Family Member: NovartisCharles D. LopezConsulting or Advisory Role: Boston Scientific, Celgene, Boston Biomedical, Pfizer, Exelixis, Astellas Pharma Research Funding: Taiho Pharmaceutical Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: RenovoRxLisa M. CoussensEmployment: Oregon Health & Science University (OHSU) Honoraria: Prospect Creek Foundation, Lustgarten Foundation for Pancreatic Cancer Research, Syndax Pharmaceuticals, Inc: External Advisory Board, Carisma Therapeutics Inc: Scientific Advisory Board, Verseau Therapeutics, Inc, Scientific Advisory Board, Zymeworks, Inc, Scientific Advisory Board, CytomX Therapeutics, Inc, Kineta Inc, (P30) Koch Institute for Integrated Cancer Research, Massachusetts Inst. of Tech, (P30) Salk Institute Cancer Center, Bloomberg-Kimmel Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy, Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center at Johns Hopkins, Dana Farber Cancer Center Breast SPORE, (P30) Dana Farber/Harvard Cancer Center, (P30) University of California, San Diego Moores Cancer Center, Starr Cancer Consortium, Lustgarten Foundation for Pancreatic Cancer Research, Therapeutics Working Group, NIH/NCI-Frederick National Laboratory Advisory Committee (FNLAC), Susan G Komen Foundation, Komen Scholar Consulting or Advisory Role: Cell Signaling Technologies, Pharmacyclics, CytomX Therapeutics, Syndax, Carisma Therapeutics, Verseau Therapeutics, Zymeworks, Kineta, Inc, Abbvie, Shasqi Inc Research Funding: Syndax Pharmaceuticals Inc, Pharmacyclics, Cell Signaling Technologies, Innate Pharma, Deciphera Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Cell Signaling Technologies, AstraZeneca, Pharmacyclics, Verseau, Carisma Therapeutics, CytomX Therapeutics, Zymeworks Other Relationship: Prospect Creek Foundation, Lustgarten Foundation for Pancreatic Cancer Research, (P30) Koch Institute for Integrated Cancer Research, Massachusetts Inst. of Tech. (2012-present; honorarium), (P30) Salk Institute Cancer Center: (2016-2020; honorarium), Bloomberg-Kimmel Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy, Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center at Johns Hopkins: (2016-present; honorarium), Dana Farber Cancer Center Breast SPORE: (2017-present; honorarium), (P30) Dana Farber/Harvard Cancer Center: (2019-present; honorarium), (P30) University of California, San Diego Moores Cancer Center (2019-present; honorarium), Cancer Research Institute (CRI): (2013-present; unpaid), The V Foundation for Cancer Research): (2013-present; unpaid), Starr Cancer Consortium: (2011-present, honorarium), Lustgarten Foundation for Pancreatic Cancer Research, Therapeutics Working Group: (2019-present; paid), NIH/NCI-Frederick National Laboratory Advisory Committee (FNLAC): (2016-present; daily honorarium), Susan G Komen Foundation, Komen Scholar (2020 – 2023; honorarium)Rosalie C. SearsConsulting or Advisory Role: Novartis No other potential conflicts of interest were reported
Figures
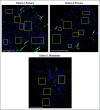
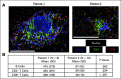
References
-
- Hidalgo M, Cascinu S, Kleeff J, et al. Addressing the challenges of pancreatic cancer: Future directions for improving outcomes Pancreatology 158–182015 - PubMed
-
- Cancer Facts & Figures 2018. American Cancer Society; 2018. https://www.cancer.org/research/cancer-facts-statistics/all-cancer-facts...
-
- Conroy T, Hammel P, Hebbar M, et al. FOLFIRINOX or gemcitabine as adjuvant therapy for pancreatic cancer N Engl J Med 3792395–24062018 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

