Implantable cardiac pacemaker failure by cumulative dose effects of flattening filter free beams
- PMID: 34036327
- PMCID: PMC8273809
- DOI: 10.1093/jrr/rrab041
Implantable cardiac pacemaker failure by cumulative dose effects of flattening filter free beams
Abstract
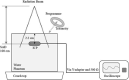
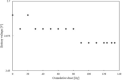
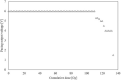
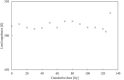
Cumulative dose effects, which are one of the main causes of errors that occur when an implantable cardiac pacemaker (ICP) is irradiated with ionizing radiation, induce permanent failure in ICPs. Although flattening filter free (FFF) beams, which are often used in stereotactic radiotherapy, are known to have different characteristics from conventional (with flattening filter [WFF]) beams, the cumulative dose effects on ICPs with FFF beams have been under-investigated. This study investigates ICP failure induced by cumulative dose effects of FFF beams. When the ICP placed in the center of the irradiation field was irradiated with 10 MV-FFF at 24 Gy/min, the cumulative dose at which failure occurred was evaluated on the basis of the failure criteria associated with high cumulative dose as described in the American Association of Physicists in Medicine Task Group 203. The ICP failures such as a mild battery depletion at a cumulative dose of 10 Gy, pacing-output voltage change >25% at a cumulative dose of 122 Gy, and the loss of telemetry capability at cumulative dose 134 Gy were induced by cumulative dose effects. The cumulative doses by which the cumulative dose effects of FFF beams induced ICP failure were not very different from those reported in previous studies with WFF beams. Therefore, radiotherapy with FFF beams (and WFF beams) for patients with ICP requires appropriate management for minimizing the cumulative dose effects.
Keywords: FFF beams; cumulative dose effects; failure; implantable cardiac pacemaker (ICP); radiotherapy.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Japanese Radiation Research Society and Japanese Society for Radiation Oncology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of X-ray dose rates higher than 8 Gy/min on the functioning of cardiac implantable electronic devices.J Radiat Res. 2020 May 22;61(3):419-425. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rraa016. J Radiat Res. 2020. PMID: 32253430 Free PMC article.
-
MO-A-BRB-02: Facts and Fiction of Flattening Filter Free (FF-FFF) X-Rays Beams.Med Phys. 2012 Jun;39(6Part20):3861-3862. doi: 10.1118/1.4735765. Med Phys. 2012. PMID: 28517518
-
Impact of flattening-filter-free radiation on the clonogenic survival of astrocytic cell lines.Strahlenther Onkol. 2015 Jul;191(7):590-6. doi: 10.1007/s00066-015-0823-5. Epub 2015 Mar 13. Strahlenther Onkol. 2015. PMID: 25764245
-
[A Proposal for the Absorbed Dose to Water Dosimetry for Flattening Filter-free Beams].Igaku Butsuri. 2016;36(2):79-84. doi: 10.11323/jjmp.36.2_79. Igaku Butsuri. 2016. PMID: 28428458 Review. Japanese.
-
Current status and future perspective of flattening filter free photon beams.Med Phys. 2011 Mar;38(3):1280-93. doi: 10.1118/1.3554643. Med Phys. 2011. PMID: 21520840 Review.
Cited by
-
Risk of cardiac implantable device malfunction in cancer patients receiving proton therapy: an overview.Front Oncol. 2023 Jul 4;13:1181450. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1181450. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37469405 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Safety Review of Radiotherapy for Tumor Patients with Implantable Cardiac Pacemaker.Acta Cardiol Sin. 2023 Nov;39(6):807-816. doi: 10.6515/ACS.202311_39(6).20230828A. Acta Cardiol Sin. 2023. PMID: 38022419 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sundar S, Symonds RP, Deehan C. Radiotherapy to patients with artificial cardiac pacemakers. Cancer Treat Rev 2005;31:474–86. - PubMed
-
- Wilkoff BL, Auricchio A, Brugada J et al. HRS/EHRA expert consensus on the monitoring of cardiovascular implantable electronic devices (CIEDs): description of techniques, indications, personnel, frequency and ethical considerations. Europace 2008;10:707–25. - PubMed
-
- Last A. Radiotherapy in patients with cardiac pacemakers. Br J Radiol 1998;71:4–10. - PubMed
-
- Miften M, Mihailidis D, Kry SF et al. Management of radiotherapy patients with implanted cardiac pacemakers and defibrillators: a report of the AAPM TG-203. Med Phys 2019;46:e757–88. - PubMed
-
- Nemec J. Runaway implantable defibrillator—a rare complication of radiation therapy. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 2007;30:716–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

