Simultaneous right-sided nephrectomy with orthotopic liver and kidney transplantation-An alternative method for patients with autosomal dominant polycystic liver and kidney disease
- PMID: 34036408
- PMCID: PMC8481182
- DOI: 10.1007/s00423-021-02206-9
Simultaneous right-sided nephrectomy with orthotopic liver and kidney transplantation-An alternative method for patients with autosomal dominant polycystic liver and kidney disease
Abstract
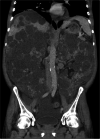
Purpose: In patients suffering from autosomal dominant polycystic liver and kidney disease (ADPLKD), combined organ transplantation often poses a technical challenge due to the large volume of both organs. To simplify the transplantation procedure by improving the exposure of anatomical structures, we introduce a novel surgical technique of orthotopic liver and kidney transplantation.
Methods: The modified simultaneous liver and kidney transplantation technique via a right-sided L-incision included three steps: (1) right-sided nephrectomy in the recipient followed by (2) orthotopic liver transplantation in cava replacement technique and (3) the orthotopic kidney transplantation with arterial reconstruction to the right common iliac artery.
Results: In total, seven patients with ADPLKD were transplanted by using the modified transplantation technique. The mean operation time was 342.43 min (±68.77). Postoperative patients were treated for 6.28 days (±2.50) in the intensive care unit and were discharged from the surgical ward approximately 28 days (±5.66) after the operation with normal graft function. Complications associated with the use of the modified technique, such as bleeding, anastomotic stenosis, biloma, or urinoma, did not occur.
Conclusion: Modified simultaneous liver and kidney transplantation is a safe alternative for patients with ADPLKD. By combining right-sided nephrectomy and orthotopic graft transplantation, the approach optimizes the exposure of anatomical structures and simplifies the transplantation procedure. Additionally, the modified transplantation technique does not require a particular organ explantation procedure and can be applied for all liver and kidney grafts.
Keywords: Autosomal dominant polycystic liver and kidney disease; Kidney transplantation; Liver transplantation.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Simultaneous bilateral native nephrectomy and living donor renal transplantation are successful for polycystic kidney disease: the University of Maryland experience.J Urol. 2009 Feb;181(2):724-8. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2008.10.008. Epub 2008 Dec 16. J Urol. 2009. PMID: 19091353
-
Selective, concurrent bilateral nephrectomies at renal transplantation for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.J Urol. 2007 Jun;177(6):2250-4; discussion 2254. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2007.01.146. J Urol. 2007. PMID: 17509331
-
One hundred consecutive kidney transplantations with simultaneous ipsilateral nephrectomy in patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013 Feb;28(2):466-71. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfs118. Epub 2012 Oct 4. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013. PMID: 23042709
-
Native nephrectomy and arterial embolization of native kidney in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease patients: indications, timing and postoperative outcomes.Minerva Urol Nephrol. 2023 Feb;75(1):17-30. doi: 10.23736/S2724-6051.22.04972-2. Epub 2022 Sep 12. Minerva Urol Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 36094388
-
Bilateral Nephrectomy for Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease and Timing of Kidney Transplant: A Review of the Technical Advances in Surgical Management of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Disease.Exp Clin Transplant. 2015 Jun;13(3):209-13. Exp Clin Transplant. 2015. PMID: 26086830 Review.
Cited by
-
Surgical Management of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease: Principles and Current Practice.JNMA J Nepal Med Assoc. 2023 May 1;61(261):485-491. doi: 10.31729/jnma.8159. JNMA J Nepal Med Assoc. 2023. PMID: 37203894 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ueno T, Barri YM, Netto GJ, Martin A, Onaca N, Sanchez EQ, Chinnakotla S, Randall HB, Dawson S, Levy MF, Goldstein RM, Klintmalm GB. Liver and kidney transplantation for polycystic liver and kidney-renal function and outcome. Transplantation. 2006;82(4):501–507. doi: 10.1097/01.tp.0000231712.75645.7a. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kirchner GI, Rifai K, Cantz T, Nashan B, Terkamp C, Becker T, Strassburg C, Barg-Hock H, Wagner S, Lück R, Klempnauer J, Manns MP. Outcome and quality of life in patients with polycystic liver disease after liver or combined liver-kidney transplantation. Liver Transpl [Internet] 2006;12(8):1268–1277. doi: 10.1002/lt.20780. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chapman AB, Bost JE, Torres VE, Guay-Woodford L, Bae KT, Landsittel D, Li J, King BF, Martin D, Wetzel LH, Lockhart ME, Harris PC, Moxey-Mims M, Flessner M, Bennett WM, Grantham JJ. Kidney volume and functional outcomes in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol [Internet] 2012;7(3):479–486. doi: 10.2215/CJN.09500911. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

