Endocrine-related adverse events in a large series of cancer patients treated with anti-PD1 therapy
- PMID: 34036513
- PMCID: PMC8440282
- DOI: 10.1007/s12020-021-02750-w
Endocrine-related adverse events in a large series of cancer patients treated with anti-PD1 therapy
Abstract
Purpose: Immune checkpoint inhibitors have opened a new scenario in the treatment of cancer. These agents can elicit adverse events, which may affect different systems and organs, including the endocrine system. The aims of this study were to evaluate the impact of the anti-PD-1 molecules nivolumab and pembrolizumab on endocrine toxicity and on patient outcome.
Methods: A retrospective and multicentre study was designed, which involved a total of 251 patients affected by different tumors (mostly non-small cell lung cancer, 68.92% and melanoma, 24.30%) and treated with the PD-1 inhibitors nivolumab (61.35%) or pembrolizumab (38.65%) for up to 60 months. Clinical and biochemical data were recorded until July 31, 2020.
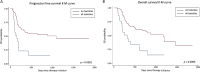
Results: Endocrine toxicity occurred in 70 out of 251 patients (27.89%). It was mostly related to thyroid dysfunction and in 75% of cases occurred within 6 months from the beginning of therapy. A previous endocrine morbidity and female gender were predictors of endocrine toxicity. There was no association between endocrine dysfunction and patient outcome. However, when all toxicities (i.e., endocrine and non endocrine) were considered, a significant association with progression-free survival and overall survival was found.
Conclusions: Thyroid alterations are frequently observed in cancer patients treated with anti PD-1 drugs, particularly in women and in the presence of a previous endocrinopathy. We suggest that regular thyroid assessment should be performed in these patients, especially in the first months of therapy. Finally, the onset of side effects, related to anti PD-1 agents, appears to be associated with a better outcome.
Keywords: Anti PD-1; Cancer; Endocrine toxicity; Immunotherapy.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Endocrine toxicity in cancer patients treated with nivolumab or pembrolizumab: results of a large multicentre study.J Endocrinol Invest. 2020 Mar;43(3):337-345. doi: 10.1007/s40618-019-01112-8. Epub 2019 Sep 21. J Endocrinol Invest. 2020. PMID: 31542865
-
Nivolumab-induced thyroid dysfunction in patients with lung cancer.Endocrinol Diabetes Nutr (Engl Ed). 2019 Jan;66(1):26-34. doi: 10.1016/j.endinu.2018.05.005. Epub 2018 Jun 15. Endocrinol Diabetes Nutr (Engl Ed). 2019. PMID: 29910159 English, Spanish.
-
Overt Thyroid Dysfunction and Anti-Thyroid Antibodies Predict Response to Anti-PD-1 Immunotherapy in Cancer Patients.Thyroid. 2020 Jul;30(7):966-973. doi: 10.1089/thy.2019.0726. Epub 2020 Apr 23. Thyroid. 2020. PMID: 32151195
-
New insight in endocrine-related adverse events associated to immune checkpoint blockade.Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020 Jan;34(1):101370. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2019.101370. Epub 2019 Dec 11. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020. PMID: 31983543 Review.
-
Toxicity management with combination chemotherapy and programmed death 1/programmed death ligand 1 inhibitor therapy in advanced lung cancer.Cancer Treat Rev. 2020 Apr;85:101979. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2020.101979. Epub 2020 Feb 4. Cancer Treat Rev. 2020. PMID: 32078962 Review.
Cited by
-
Thyroid dysfunction induced by anti-PD-1 therapy is associated with a better progression-free survival in patients with advanced carcinoma.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Dec;149(18):16501-16510. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-05364-z. Epub 2023 Sep 15. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37715029 Free PMC article.
-
Management of Endocrine and Metabolic Toxicities of Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitors: From Clinical Studies to a Real-Life Scenario.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Dec 30;15(1):246. doi: 10.3390/cancers15010246. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36612243 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune checkpoint inhibitors and endocrinopathies in pediatric brain tumor patients.J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2024 Dec 16;38(1):58-64. doi: 10.1515/jpem-2024-0243. Print 2025 Jan 29. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2024. PMID: 39680426 Free PMC article.
-
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors-Induced Endocrinopathies: Assessment, Management and Monitoring in a Comprehensive Cancer Centre.Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2024 Jul;7(4):e00505. doi: 10.1002/edm2.505. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2024. PMID: 38932429 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges and pitfalls in the management of endocrine toxicities from immune checkpoint inhibitors: a case presentation of synchronous thyrotoxicosis and primary adrenal insufficiency in a melanoma patient.Hormones (Athens). 2024 Dec;23(4):759-764. doi: 10.1007/s42000-024-00535-0. Epub 2024 Feb 29. Hormones (Athens). 2024. PMID: 38421588
References
-
- Wolchok JD, Neyns B, Linette G, Negrier S, Lutzky J, Thomas L, Waterfield W, Schadendorf D, Smylie M, Guthrie T, Jr, et al. Ipilimumab monotherapy in patients with pretreated advanced melanoma: a randomised, double-blind, multicentre, phase 2, dose-ranging study. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11:155–164. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70334-1. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

