Acute events in children with sickle cell disease in Italy during the COVID-19 pandemic: useful lessons learned
- PMID: 34036565
- PMCID: PMC8239759
- DOI: 10.1111/bjh.17546
Acute events in children with sickle cell disease in Italy during the COVID-19 pandemic: useful lessons learned
Keywords: COVID-19; Italy; Vaso-occlusive crisis; acute chest; children; sickle cell disease.
Figures
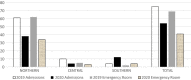
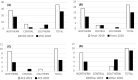
References
-
- Megna R. First month of the epidemic caused by COVID‐19 in Italy: current status and real‐time outbreak development forecast. Glob Health Res Policy. 2020;5:43;eCollection 2020. https://ghrp.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s41256‐020‐00170‐3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Colombatti R, Palazzi G, Masera N, Notarangelo LD, Bonetti E, Samperi P, et al. Hydroxyurea prescription, availability and use for children with sickle cell disease in Italy: results of a National Multicenter survey. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2018;65:e26774 - PubMed
-
- Piel FB, Steinberg MH, Rees DC. Sickle cell disease. N Engl J Med. 2017;376:1561–73. - PubMed
-
- Po’ C, Colombatti R, Cirigliano A, Dalt LD, Agosto C, Benini F, et al. The management of sickle cell pain in the emergency department: a priority for health systems. Clin J Pain. 2013;29:60–3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

