Effects of bradykinin on voltage-gated KV 4 channels in muscle dorsal root ganglion neurons of rats with experimental peripheral artery disease
- PMID: 34036586
- PMCID: PMC8284427
- DOI: 10.1113/JP281704
Effects of bradykinin on voltage-gated KV 4 channels in muscle dorsal root ganglion neurons of rats with experimental peripheral artery disease
Abstract
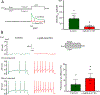
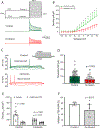
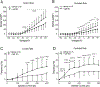
Key points: During exercise, bradykinin (BK), a muscle metabolite in ischaemic muscles, exaggerates autonomic responses to activation of muscle afferent nerves in peripheral artery disease (PAD). We examined whether BK inhibits activity of KV 4 channels in muscle afferent neurons of PAD rats induced by femoral artery occlusion. We demonstrated that: 1) femoral occlusion attenuates KV 4 currents in dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons innervating the hindlimb muscles and decreases the threshold of action potential firing; 2) BK has a greater inhibitory effect on KV 4 currents in muscle DRG neurons of PAD rats; and 3) expression of KV 4.3 is downregulated in DRGs of PAD rats and inhibition of KV 4.3 significantly decreases activity of KV 4 currents in muscle DRG neurons. Femoral artery occlusion-induced limb ischaemia and/or ischaemia-induced metabolites (i.e. BK) inhibit activity of KV 4 channels in muscle afferent neurons and this is likely involved in the exaggerated exercise pressor reflex in PAD.
Abstract: Muscle afferent nerve-activated reflex sympathetic nervous and blood pressure responses are exaggerated during exercise in patients with peripheral artery diseases (PAD) and in PAD rats induced by femoral artery occlusion. However, the precise signalling pathways and molecular mediators responsible for these abnormal autonomic responses in PAD are poorly understood. A-type voltage-gated K+ (KV ) channels are quintessential regulators of cellular excitability in the various tissues. Among KV channels, KV 4 (i.e. KV 4.1 and KV 4.3) in primary sensory neurons mainly participate in physiological functions in regulation of mechanical and chemical sensation. However, little is known about the role of KV 4 in regulating neuronal activity in muscle afferent neurons of PAD. In addition, bradykinin (BK) is considered as a muscle metabolite contributing to the exaggerated exercise pressor reflex in PAD rats with femoral artery occlusion. Our data demonstrated that: 1) KV 4 currents are attenuated in dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons innervating the hindlimb muscles of PAD rats, along with a decreasing threshold of action potential firing; 2) KV 4 currents are inhibited by application of BK onto muscle DRG neurons of PAD rats to a greater degree; and 3) expression of KV 4.3 is downregulated in the DRGs of PAD rats and KV 4.3 channel is a major contributor to the activity of KV 4 currents in muscle DRG neurons. In conclusion, data suggest that femoral artery occlusion-induced limb ischaemia and/or ischaemia-induced metabolites (i.e. BK) inhibit the activity of KV 4 channels in muscle afferent neurons likely leading to the exaggerated exercise pressor reflex observed in PAD.
Keywords: A-type voltage-gated K+ channels; bradykinin; dorsal root ganglion; peripheral artery disease.
© 2021 The Authors. The Journal of Physiology © 2021 The Physiological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
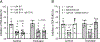
Similar articles
-
Voltage-gated potassium channel dysfunction in dorsal root ganglia contributes to the exaggerated exercise pressor reflex in rats with chronic heart failure.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2021 Aug 1;321(2):H461-H474. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00256.2021. Epub 2021 Jul 16. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34270374 Free PMC article.
-
KV4 channels in isolectin B4 muscle dorsal root ganglion neurons of rats with experimental peripheral artery disease: effects of bradykinin B1 and B2 receptors.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2022 Nov 1;323(5):R616-R627. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00117.2022. Epub 2022 Sep 12. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36094447 Free PMC article.
-
IL-6 signaling pathway contributes to exercise pressor reflex in rats with femoral artery occlusion in association with Kv4 activity in muscle afferent nerves.Physiol Rep. 2021 Jul;9(13):e14935. doi: 10.14814/phy2.14935. Physiol Rep. 2021. PMID: 34231965 Free PMC article.
-
Sympathetic Nerve Activity and Blood Pressure Response to Exercise in Peripheral Artery Disease: From Molecular Mechanisms, Human Studies, to Intervention Strategy Development.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 13;23(18):10622. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810622. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142521 Free PMC article. Review.
-
K+ Channels in Primary Afferents and Their Role in Nerve Injury-Induced Pain.Front Cell Neurosci. 2020 Sep 17;14:566418. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2020.566418. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33093824 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
NaV1.9 current in muscle afferent neurons is enhanced by substances released during muscle activity.J Neurophysiol. 2022 Oct 1;128(4):739-750. doi: 10.1152/jn.00116.2022. Epub 2022 Aug 31. J Neurophysiol. 2022. PMID: 36043704 Free PMC article.
-
Muscle afferent ASIC3 upregulation mediates the exacerbated exercise pressor reflex in male rats following hindlimb ischemia-reperfusion.Physiol Rep. 2025 Jul;13(13):e70457. doi: 10.14814/phy2.70457. Physiol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40635407 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics of acid-sensing ion channel currents in male rat muscle dorsal root ganglion neurons following ischemia/reperfusion.Physiol Rep. 2023 Mar;11(6):e15654. doi: 10.14814/phy2.15654. Physiol Rep. 2023. PMID: 36967457 Free PMC article.
-
Voltage-gated potassium channel dysfunction in dorsal root ganglia contributes to the exaggerated exercise pressor reflex in rats with chronic heart failure.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2021 Aug 1;321(2):H461-H474. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00256.2021. Epub 2021 Jul 16. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34270374 Free PMC article.
-
KV4 channels in isolectin B4 muscle dorsal root ganglion neurons of rats with experimental peripheral artery disease: effects of bradykinin B1 and B2 receptors.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2022 Nov 1;323(5):R616-R627. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00117.2022. Epub 2022 Sep 12. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36094447 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ambrosino P, Soldovieri MV, Di Zazzo E, Paventi G, Iannotti FA, Mosca I, Miceli F, Franco C, Canzoniero LMT & Taglialatela M. (2019). Activation of Kv7 Potassium Channels Inhibits Intracellular Ca(2+) Increases Triggered By TRPV1-Mediated Pain-Inducing Stimuli in F11 Immortalized Sensory Neurons. Int J Mol Sci 20. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anand SS, Caron F, Eikelboom JW, Bosch J, Dyal L, Aboyans V, Abola MT, Branch KRH, Keltai K, Bhatt DL, Verhamme P, Fox KAA, Cook-Bruns N, Lanius V, Connolly SJ & Yusuf S. (2018). Major Adverse Limb Events and Mortality in Patients With Peripheral Artery Disease: The COMPASS Trial. J Am Coll Cardiol 71, 2306–2315. - PubMed
-
- Baccelli G, Reggiani P, Mattioli A, Corbellini E, Garducci S & Catalano M. (1999). The exercise pressor reflex and changes in radial arterial pressure and heart rate during walking in patients with arteriosclerosis obliterans. Angiology 50, 361–374. - PubMed
-
- Barnett MW & Larkman PM. (2007). The action potential. Pract Neurol 7, 192–197. - PubMed
-
- Basbaum AI & Woolf CJ. (1999). Pain. Curr Biol 9, R429–431. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

