Sparse precontrast T1 mapping for high-resolution whole-brain DCE-MRI
- PMID: 34036658
- PMCID: PMC8362109
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.28849
Sparse precontrast T1 mapping for high-resolution whole-brain DCE-MRI
Abstract
Purpose: To develop and evaluate an efficient precontrast T1 mapping technique suitable for quantitative high-resolution whole-brain dynamic contrast-enhanced-magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI).
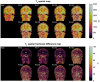
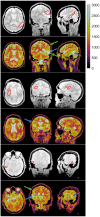
Methods: Variable flip angle (VFA) T1 mapping was considered that provides 1 × 1 × 2 mm3 resolution to match a recent high-resolution whole-brain DCE-MRI protocol. Seven FAs were logarithmically spaced from 1.5° to 15°. T1 and M0 maps were estimated using model-based reconstruction. This approach was evaluated using an anatomically realistic brain tumor digital reference object (DRO) with noise-mimicking 3T neuroimaging and fully sampled data acquired from one healthy volunteer. Methods were also applied on fourfold prospectively undersampled VFA data from 13 patients with high-grade gliomas.
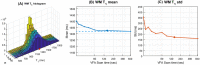
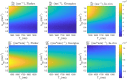
Results: T1 -mapping precision decreased with undersampling factor R, althoughwhereas bias remained small before a critical R. In the noiseless DRO, T1 bias was <25 ms in white matter (WM) and <11 ms in brain tumor (BT). T1 standard deviation (SD) was <119.5 ms in WM (coefficient of variation [COV] ~11.0%) and <253.2 ms in BT (COV ~12.7%). In the noisy DRO, T1 bias was <50 ms in WM and <30 ms in BT. For R ≤ 10, T1 SD was <107.1 ms in WM (COV ~9.9%) and <240.9 ms in BT (COV ~12.1%). In the healthy subject, T1 bias was <30 ms for R ≤ 16. At R = 4, T1 SD was 171.4 ms (COV ~13.0%). In the prospective brain tumor study, T1 values were consistent with literature values in WM and BT.
Conclusion: High-resolution whole-brain VFA T1 mapping is feasible with sparse sampling, supporting its use for quantitative DCE-MRI.
Keywords: T1 mapping; brain tumor; model-based reconstruction; quantitative dynamic contrast-enhanced-magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI); sparse sampling.
© 2021 The Authors. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Coauthor R. Marc Lebel is an employee of GE Healthcare. The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Tofts PS, Brix G, Buckley DL, et al. Estimating kinetic parameters from dynamic contrast‐enhanced t1‐weighted MRI of a diffusable tracer: standardized quantities and symbols. J Magn Reson Imaging. 1999;10:223‐232. - PubMed
-
- Sourbron SP, Buckley DL. On the scope and interpretation of the Tofts models for DCE‐MRI. Magn Reson Med. 2011;66:735‐745. - PubMed
-
- O’Connor JPB, Jackson A, Parker GJM, Roberts C, Jayson GC. Dynamic contrast‐enhanced MRI in clinical trials of antivascular therapies. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2012;9:167‐177. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

