Cellular and humoral response after MRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in kidney transplant recipients
- PMID: 34036720
- PMCID: PMC8222867
- DOI: 10.1111/ajt.16701
Cellular and humoral response after MRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in kidney transplant recipients
Abstract
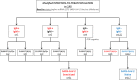
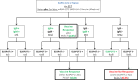
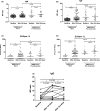
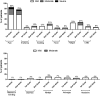
According to preliminary data, seroconversion after mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccination might be unsatisfactory in Kidney Transplant Recipients (KTRs). However, it is unknown if seronegative patients develop at least a cellular response that could offer a certain grade of protection against SARS-CoV-2. To answer this question, we prospectively studied 148 recipients of either kidney (133) or kidney-pancreas (15) grafts with assessment of IgM/IgG spike (S) antibodies and ELISpot against the nucleocapside (N) and the S protein at baseline and 2 weeks after receiving the second dose of the mRNA-1273 (Moderna) vaccine. At baseline, 31 patients (20.9%) had either IgM/IgG or ELISpot positivity and were considered to be SARS-CoV-2-pre-immunized, while 117 (79.1%) patients had no signs of either cellular or humoral response and were considered SARS-CoV-2-naïve. After vaccination, naïve patients who developed either humoral or cellular response were finally 65.0%, of which 29.9% developed either IgG or IgM and 35.0% S-ELISpot positivity. Factors associated with vaccine unresponsiveness were diabetes and treatment with antithymocytes globulins during the last year. Side effects were consistent with that of the pivotal trial and no DSAs developed after vaccination. In conclusion, mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine elicits either cellular or humoral response in almost two thirds of KTRs.
Keywords: clinical research / practice; infection and infectious agents - viral; infectious disease; kidney transplantation / nephrology; vaccine.
© 2021 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. WHO coronavirus dashboard. https://covid19.who.int/. Accessed April 14, 2021.
-
- US Department of Health and Human Services. BARDA’s expanding COVID-19 medical countermeasure portfolio. https://www.medicalcountermeasures.gov/app/barda/coronavirus/COVID19.asp.... Accessed April 14, 2021.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

