Synthesis of flavour-related linalool is regulated by PpbHLH1 and associated with changes in DNA methylation during peach fruit ripening
- PMID: 34036730
- PMCID: PMC8486240
- DOI: 10.1111/pbi.13638
Synthesis of flavour-related linalool is regulated by PpbHLH1 and associated with changes in DNA methylation during peach fruit ripening
Abstract
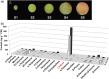
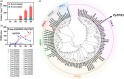
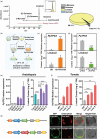
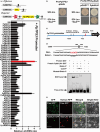
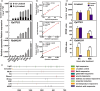
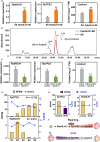
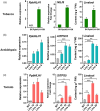
Linalool is one of the common flavour-related volatiles across the plant kingdom and plays an essential role in determining consumer liking of plant foods. Although great process has been made in identifying terpene synthase (TPS) genes associated with linalool synthesis, much less is known about regulation of this pathway. We initiated study by identifying PpTPS3 encoding protein catalysing enantiomer (S)-(+)-linalool synthesis, which is a major linalool component (˜70%) observed in ripe peach fruit. Overexpression of PpTPS3 led to linalool accumulation, while virus-induced gene silencing of PpTPS3 led to a 66.5% reduction in linalool content in peach fruit. We next identified transcription factor (TF) PpbHLH1 directly binds to E-box (CACATG) in the PpTPS3 promoter and activates its expression based on yeast one-hybrid assay and EMSA analysis. Significantly positive correlation was also observed between PpbHLH1 expression and linalool production across peach cultivars. Peach fruit accumulated more linalool after overexpressing PpbHLH1 in peach fruit and reduced approximately 54.4% linalool production after silencing this TF. DNA methylation analysis showed increased PpTPS3 expression was associated with decreased 5 mC level in its promoter during peach fruit ripening, but no reverse pattern was observed for PpbHLH1. Arabidopsis and tomato fruits transgenic for peach PpbHLH1 synthesize and accumulate higher levels of linalool compared with wild-type controls. Taken together, these results would greatly facilitate efforts to enhance linalool production and thus improve flavour of fruits.
Keywords: epigenetics; fruit aroma; linalool; transcription factor.
© 2021 The Authors. Plant Biotechnology Journal published by Society for Experimental Biology and The Association of Applied Biologists and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Boachon, B. , Junker, R.R. , Miesch, L. , Bassard, J.E. , Höfer, R. , Caillieaudeaux, R. , Seidel, D.E. et al. (2015) CYP76C1(Cytochrome P450)‐mediated linalool metabolism and the formation of volatile and soluble linalool oxides in Arabidopsis flowers: A strategy for defense against floral antagonists. Plant Cell, 27, 2972–2990. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

