Cancer cell metabolism connects epigenetic modifications to transcriptional regulation
- PMID: 34036737
- PMCID: PMC8613311
- DOI: 10.1111/febs.16032
Cancer cell metabolism connects epigenetic modifications to transcriptional regulation
Abstract
Adaptation of cellular function with the nutrient environment is essential for survival. Failure to adapt can lead to cell death and/or disease. Indeed, energy metabolism alterations are a major contributing factor for many pathologies, including cancer, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes. In particular, a primary characteristic of cancer cells is altered metabolism that promotes survival and proliferation even in the presence of limited nutrients. Interestingly, recent studies demonstrate that metabolic pathways produce intermediary metabolites that directly influence epigenetic modifications in the genome. Emerging evidence demonstrates that metabolic processes in cancer cells fuel malignant growth, in part, through epigenetic regulation of gene expression programs important for proliferation and adaptive survival. In this review, recent progress toward understanding the relationship of cancer cell metabolism, epigenetic modification, and transcriptional regulation will be discussed. Specifically, the need for adaptive cell metabolism and its modulation in cancer cells will be introduced. Current knowledge on the emerging field of metabolite production and epigenetic modification will also be reviewed. Alterations of DNA (de)methylation, histone modifications, such as (de)methylation and (de)acylation, as well as chromatin remodeling, will be discussed in the context of cancer cell metabolism. Finally, how these epigenetic alterations contribute to cancer cell phenotypes will be summarized. Collectively, these studies reveal that both metabolic and epigenetic pathways in cancer cells are closely linked, representing multiple opportunities to therapeutically target the unique features of malignant growth.
Keywords: DNA methylation; acetylation; acylation; cancer; glycolysis; histone; metabolism; methylation; oxidative phosphorylation.
© 2021 Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
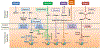
References
-
- JOHNSTON G, PRINGLE J & HARTWELL L (1977) Coordination of growth with cell division in the yeast. Exp Cell Res 105, 79–98. - PubMed
-
- Jorgensen P & Tyers M (2004) How Cells Coordinate Growth and Division. Current Biology 14, R1014–R1027. - PubMed
-
- Jorgensen P, Nishikawa JL, Breitkreutz B-J & Tyers M (2002) Systematic identification of pathways that couple cell growth and division in yeast. Science 297, 395–400. - PubMed
-
- Cai L & Tu BP (2012) Driving the Cell Cycle Through Metabolism. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 28, 59–87. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

