Redox Control of Integrin-Mediated Hepatic Inflammation in Systemic Autoimmunity
- PMID: 34036799
- PMCID: PMC8982133
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2021.0068
Redox Control of Integrin-Mediated Hepatic Inflammation in Systemic Autoimmunity
Abstract
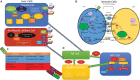
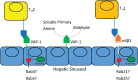
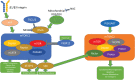
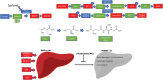
Significance: Systemic autoimmunity affects 3%-5% of the population worldwide. Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a prototypical form of such condition, which affects 20-150 of 100,000 people globally. Liver dysfunction, defined by increased immune cell infiltration into the hepatic parenchyma, is an understudied manifestation that affects up to 20% of SLE patients. Autoimmunity in SLE involves proinflammatory lineage specification in the immune system that occurs with oxidative stress and profound changes in cellular metabolism. As the primary metabolic organ of the body, the liver is uniquely capable to encounter oxidative stress through first-pass derivatization and filtering of waste products. Recent Advances: The traffic of immune cells from their development through recirculation in the liver is guided by cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) and integrins, cell surface proteins that tightly anchor cells together. The surface expression of CAMs and integrins is regulated via endocytic traffic that is sensitive to oxidative stress. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) that elicit oxidative stress in the liver may originate from the mitochondria, the cytosol, or the cell membrane. Critical Issues: While hepatic ROS production is a source of vulnerability, it also modulates the development and function of the immune system. In turn, the liver employs antioxidant defense mechanisms to protect itself from damage that can be harnessed to serve as therapeutic mechanisms against autoimmunity, inflammation, and development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Future Directions: This review is aimed at delineating redox control of integrin signaling in the liver and checkpoints of regulatory impact that can be targeted for treatment of inflammation in systemic autoimmunity. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 36, 367-388.
Keywords: Rab GTPases; T cell signaling; autoimmunity; cell adhesion molecules; endosomes; hepatic injury; immune synapse; immunity; integrins; liver; oxidative stress; reactive oxygen species; systemic lupus erythematosus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors do not have any competing financial interests to disclose.
Figures

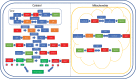
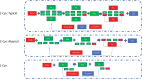
References
-
- Andres PG, Howland KC, Dresnek D, Edmondson S, Abbas AK, and Krummel MF. CD28 signals in the immature immunological synapse. J Immunol 172: 5880–5886, 2004. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

