Alternative polyadenylated mRNAs behave as asynchronous rhythmic transcription in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 34036876
- PMCID: PMC8632115
- DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2021.1933732
Alternative polyadenylated mRNAs behave as asynchronous rhythmic transcription in Arabidopsis
Abstract
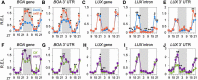
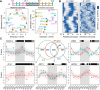
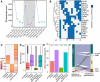
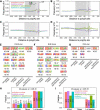
Alternative polyadenylation (APA) is a widespread post-transcriptional modification method that changes the 3' ends of transcripts by altering poly(A) site usage. However, the longitudinal transcriptomic 3' end profile and its mechanism of action are poorly understood. We applied diurnal time-course poly(A) tag sequencing (PAT-seq) for Arabidopsis and identified 3284 genes that generated both rhythmic and arrhythmic transcripts. These two classes of transcripts appear to exhibit dramatic differences in expression and translation activisty. The asynchronized transcripts derived by APA are embedded with different poly(A) signals, especially for rhythmic transcripts, which contain higher AAUAAA and UGUA signal proportions. The Pol II occupancy maximum is reached upstream of rhythmic poly(A) sites, while it is present directly at arrhythmic poly(A) sites. Integrating H3K9ac and H3K4me3 time-course data analyses revealed that transcriptional activation of histone markers may be involved in the differentiation of rhythmic and arrhythmic APA transcripts. These results implicate an interplay between histone modification and RNA 3'-end processing, shedding light on the mechanism of transcription rhythm and alternative polyadenylation.
Keywords: Pol II; Polyadenylation; diurnal rhythm; histone modification; poly(A) signal; post-transcriptional regulation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Alternative polyadenylation is involved in auxin-based plant growth and development.Plant J. 2018 Jan;93(2):246-258. doi: 10.1111/tpj.13771. Epub 2017 Dec 18. Plant J. 2018. PMID: 29155478
-
Transcriptome Analyses of FY Mutants Reveal Its Role in mRNA Alternative Polyadenylation.Plant Cell. 2019 Oct;31(10):2332-2352. doi: 10.1105/tpc.18.00545. Epub 2019 Aug 19. Plant Cell. 2019. PMID: 31427469 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide landscape of polyadenylation in Arabidopsis provides evidence for extensive alternative polyadenylation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Jul 26;108(30):12533-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1019732108. Epub 2011 Jul 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21746925 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative polyadenylation and gene expression regulation in plants.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011 May-Jun;2(3):445-58. doi: 10.1002/wrna.59. Epub 2010 Nov 9. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011. PMID: 21957029 Review.
-
Co-Transcriptional RNA Processing in Plants: Exploring from the Perspective of Polyadenylation.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 24;22(7):3300. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073300. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33804866 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
FLL2 modulates Arabidopsis development and stress tolerance via polyadenylation and CPSF73 interaction.iScience. 2025 May 7;28(6):112579. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112579. eCollection 2025 Jun 20. iScience. 2025. PMID: 40524959 Free PMC article.
-
Stress responses of plants through transcriptome plasticity by mRNA alternative polyadenylation.Mol Hortic. 2023 Sep 28;3(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s43897-023-00066-z. Mol Hortic. 2023. PMID: 37789388 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
