Effects of vitamin D-induced supernatant of placental explants from preeclamptic women on oxidative stress and nitric oxide bioavailability in human umbilical vein endothelial cells
- PMID: 34037098
- PMCID: PMC8148885
- DOI: 10.1590/1414-431X2020e11073
Effects of vitamin D-induced supernatant of placental explants from preeclamptic women on oxidative stress and nitric oxide bioavailability in human umbilical vein endothelial cells
Abstract
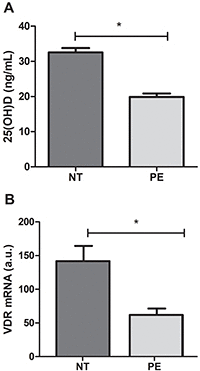
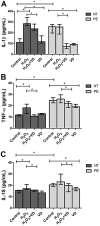
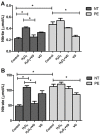
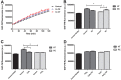
The study evaluated the effect of the supernatant of placental explants from preeclamptic (PE) and normotensive (NT) pregnant women after tissue treatment with or without vitamin D (VD) on oxidative stress and nitric oxide (NO) bioavailability in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC). Placental explants were prepared from eight NT and eight PE women, and supernatants were obtained after incubation with or without hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and/or VD. HUVEC were cultured for 24 h with supernatants, and the following parameters were analyzed in HUVEC cultures: NO, nitrate (NO3-), and nitrite (NO2-) levels, lipid peroxidation, and intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS). Results showed that the production of NO3-, NO2-, malondialdehyde (MDA), and ROS were significantly higher in HUVEC treated with explant supernatant from PE compared to NT pregnant women, while the supernatant of PE explants treated with VD led to a decrease in these parameters. A significantly high production of NO was detected in HUVEC cultured with control supernatant of NT group, and in cultures treated with supernatant of PE explants treated with VD. Taken together, these results demonstrated that cultures of placental explants from PE women with VD treatment generated a supernatant that decreased oxidative stress and increased the bioavailability of NO in endothelial cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Vitamin D decreases cell death and inflammation in human umbilical vein endothelial cells and placental explants from pregnant women with preeclampsia cultured with TNF-α.Immunol Invest. 2022 Aug;51(6):1630-1646. doi: 10.1080/08820139.2021.2017452. Epub 2021 Dec 22. Immunol Invest. 2022. PMID: 34937520
-
Vitamin D decreases expression of NLRP1 and NLRP3 inflammasomes in placental explants from women with preeclampsia cultured with hydrogen peroxide.Hum Immunol. 2022 Jan;83(1):74-80. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2021.10.002. Epub 2021 Oct 23. Hum Immunol. 2022. PMID: 34696918
-
Monocytes from preeclamptic women previously treated with silibinin attenuate oxidative stress in human endothelial cells.Hypertens Pregnancy. 2021 May;40(2):124-132. doi: 10.1080/10641955.2021.1884258. Epub 2021 Feb 14. Hypertens Pregnancy. 2021. PMID: 33586558
-
Placental calcitriol synthesis and IGF-I levels in normal and preeclamptic pregnancies.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2014 Oct;144 Pt A:44-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2013.12.014. Epub 2013 Dec 24. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24373797 Review.
-
Nitric oxide and reactive oxygen species in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Mar 2;16(3):4600-14. doi: 10.3390/ijms16034600. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25739077 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of the evolution of placental oxidative stress research from a bibliometric perspective.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Oct 17;15:1475244. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1475244. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39484166 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists Clinical Management Guidelines for Obstetrician-Gynecologists. Acog practice bulletin No. 202: Gestational hypertension and preeclampsia. Obstet Gynecol. 2009;133:e1–e25.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

