Prevalence and characterization of pain in patients with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1A
- PMID: 34037101
- PMCID: PMC9394555
- DOI: 10.1590/0004-282X-ANP-2020-0132
Prevalence and characterization of pain in patients with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1A
Abstract
Background: Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1A (CMT1A) is the most common form of hereditary neuropathy.
Objective: To investigate the prevalence and characteristics of pain in patients with CMT1A.
Methods: Nineteen patients with a diagnosis of CMT1A were evaluated between September 2018 and October 2019, and other causes of neuropathy were ruled out. The following tools were used for the pain assessment: neurological assessment, LANSS, DN4, clinical evaluation, VAS, CMTNS2 and SF-36. Statistical analysis was performed using prevalence analysis, t test, chi-square test and Spearman's rho.
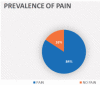
Results: The prevalence of pain was 84.2% in the sample of this study, with moderate intensity and nociceptive characteristics according to the LANSS scale (75%) and clinical evaluation (50%), but differing from DN4, which found neuropathic pain in the majority of the patients (56.2%). Mixed pain was also observed in 43.7% of the patients, according to clinical criteria. There was a statistically significant correlation between pain intensity and SF-36, thus demonstrating that the lower the pain was, the lower the impairment was, in all domains.
Conclusion: Pain is a prevalent and important symptom in CMT1A, with moderate intensity and nociceptive characteristics according to two tools, but neuropathic pain is also present, and there may even be a mixed pattern of pain. The correlation of the pain with SF-36 suggests that pain relief could provide improvements to the quality of life of these individuals.
Introdução:: A doença de Charcot-Marie-Tooth tipo 1 A (CMT1A) é a forma mais comum de neuropatia hereditária.
Objetivo:: Investigar a prevalência e as características de dor nos pacientes com a doença de CMT1A.
Métodos:: Dezenove pacientes com diagnóstico de CMT1A foram avaliados de setembro 2018 a outubro de 2019, e outras causas de neuropatia foram excluídas. As seguintes ferramentas foram utilizadas para avaliar a dor: avaliação neurológica, LANSS, DN4, avaliação clínica, EVA, CMTNS2 e SF-36. A análise estatística foi realizada pelo teste de análise de prevalência, bem como pelos testes T, do qui-quadrado e rô de Sperman.
Resultados:: A prevalência de dor foi de 84,2% na amostra do estudo, com intensidade moderada e características nociceptivas de acordo com a escala LANSS (75%) e a avaliação clínica (50%), diferentemente da escala DN4, que encontrou dor neuropática na maioria dos pacientes (56,2%). Dor mista também foi verificada em 43,7% dos pacientes, de acordo com os critérios clínicos. Houve significância estatística da correlação entre a intensidade da dor e o SF-36, demonstrando que quanto menor a dor, menor o comprometimento em todos os domínios.
Conclusão:: A dor é um sintoma prevalente e relevante na CMT1A, com intensidade moderada e características nociceptivas de acordo com duas ferramentas, mas dor neuropática também está presente, e ainda pode haver padrão misto de dor. A correlação da dor com SF-36 sugere que o alívio da dor pode proporcionar melhorias na qualidade de vida desses indivíduos.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- 1. Piscosquito G, Reilly MM, Schenone A, Fabrizi GM, Cavallaro T, Santoro L, et al. Is overwork weakness relevant in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2014 Dec;85(12):1354-8. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2014-307598 - PubMed
- Piscosquito G, Reilly MM, Schenone A, Fabrizi GM, Cavallaro T, Santoro L, et al. Is overwork weakness relevant in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2014 Dec;85(12):1354–1358. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2014-307598. - DOI - PubMed
-
- 2. Saporta MA. Charcot Tooth Disease and Other Inherite d Neuropathies. Continuum (Minneap Minn). 2014 Oct;20(5 Peripheral Nervous System Disorders):1208-25. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.CON.0000455885.37169.4c - PubMed
- Saporta MA. Charcot Tooth Disease and Other Inherite d Neuropathies. Continuum (Minneap Minn) 2014 Oct;20(5 Peripheral Nervous System Disorders):1208–1225. doi: 10.1212/01.CON.0000455885.37169.4c. - DOI - PubMed
-
- 3. Kang PB. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease: genetics, clinical features, and diagnosis; 2018. Available from: https://www.uptodate.com
- Kang PB. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease: genetics, clinical features, and diagnosis. 2018. https://www.uptodate.com.
-
- 4. Berciano J, García A, Gallardo E, Peeters K, Pelayo-Negro AL, Álvarez-Paradelo S, et al. Intermediate Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease: an electrophysiological reappraisal and systematic review. J Neurol. 2017 Aug;264(8):1655-77. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-017-8474-3 - PubMed
- Berciano J, García A, Gallardo E, Peeters K, Pelayo-Negro AL, Álvarez-Paradelo S, et al. Intermediate Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease: an electrophysiological reappraisal and systematic review. J Neurol. 2017 Aug;264(8):1655–1677. doi: 10.1007/s00415-017-8474-3. - DOI - PubMed
-
- 5. Marques Junior W, Freitas MR, Nascimento OJM, Oliveira AB, Calia L, Melo A, et al. 7p duplicated Charcot-Marie-Tooth 1A Characteristics of a new population. J Neurol. 2005 Aug;252(8):972-9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-005-0797-9 - PubMed
- Marques W, Junior, Freitas MR, Nascimento OJM, Oliveira AB, Calia L, Melo A, et al. 7p duplicated Charcot-Marie-Tooth 1A Characteristics of a new population. J Neurol. 2005 Aug;252(8):972–979. doi: 10.1007/s00415-005-0797-9. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical