COVID-19 Cross-Infection Rate After Surgical Procedures: Incidence and Outcome
- PMID: 34037248
- PMCID: PMC8242479
- DOI: 10.1002/lary.29667
COVID-19 Cross-Infection Rate After Surgical Procedures: Incidence and Outcome
Abstract
Objectives/hypothesis: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARSCoV-2) is transmitted by droplet as well as airborne infection. Surgical patients are vulnerable to the infection during their hospital admission. Some surgical procedures are classified as aerosol generating (AGP).
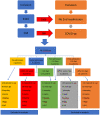
Study design: Retrospective observational study of four specialties associates with known AGP's during the 4 months of the first wave of UK COVID-19 epidermic to identify post-surgical cross-infection with SARSCoV-2 within 14 days of a procedure.
Methods: Retrospective observational study in a tertiary healthcare center of four specialties associates with known AGP's during the 4 months of the first wave of UK COVID-19 epidermic to identify post-surgical cross-infection with SARSCoV-2 within 14 days of a procedure.
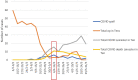
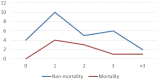
Results: There were 3,410 procedures reported during this period. The overall cross-infection rate from tested patients was 1.3% (4 patients), that is, 0.11% of all operations over 4 months. Ear, nose, and throat carried slightly higher rate of infection (0.4%) than gastroenterology (0.08%). The mortality rate was 0.3% (one gastroenterology patient from 304 positive cases) compared to 0% if surgery performed after recovery from SARSCoV-2 and 37.5% when surgery was conducted during the incubation period of the disease. Routine preoperative rapid screening tests and self-isolation are crucial to avoid the risk of cross-infection. Patients with underlying malignancy or receiving chemotherapy were more prone to pulmonary complications and mortality.
Conclusion: The risk of SARS-COV-2 cross-infection after surgical procedure is very low. Preoperative screening and self-isolation together with personal protective measures should be in place to minimize the cross-infection.
Level of evidence: 4 Laryngoscope, 131:E2749-E2754, 2021.
Keywords: SARSCoV-2; mortality; outcome; surgery.
© 2021 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- WHO Director‐General's opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID‐19 ‐ 11 March 2020. Available at: https://www.who.int/director-general/speeches/detail/who-director-genera.... Accessed March 21, 2021.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous