Clinical Study of Single-Stranded Oligonucleotide RO7062931 in Healthy Volunteers and Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B
- PMID: 34037271
- PMCID: PMC9291828
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.31920
Clinical Study of Single-Stranded Oligonucleotide RO7062931 in Healthy Volunteers and Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B
Abstract
Background and aims: RO7062931 is an N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc)-conjugated single-stranded locked nucleic acid oligonucleotide complementary to HBV RNA. GalNAc conjugation targets the liver through the asialoglycoprotein receptor (ASGPR). This two-part phase 1 study evaluated the safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of RO7062931 in healthy volunteers and patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB) who were virologically suppressed.
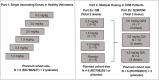
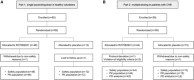
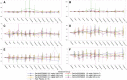
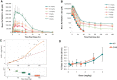
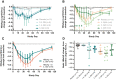
Approach and results: Part 1 was a single ascending dose study in healthy volunteers randomized to receive a single RO7062931 dose (0.1-4.0 mg/kg), or placebo. Part 2 was a multiple ascending dose study in patients with CHB randomized to receive RO7062931 at 0.5, 1.5, or 3.0 mg/kg or placebo every month for a total of 2 doses (Part 2a) or RO7062931 at 3.0 mg/kg every 2 weeks, 3.0 mg/kg every week (QW), or 4.0 mg/kg QW or placebo for a total of 3-5 doses (Part 2b). Sixty healthy volunteers and 59 patients received RO7062931 or placebo. The majority of adverse events (AEs) reported were mild in intensity. Common AEs included self-limiting injection site reactions and influenza-like illness. Supradose-proportional increases in RO7062931 plasma exposure and urinary excretion occurred at doses ≥3.0 mg/kg. In patients with CHB, RO7062931 resulted in dose-dependent and time-dependent reduction in HBsAg versus placebo. The greatest HBsAg declines from baseline were achieved with the 3.0 mg/kg QW dose regimen (mean nadir ~0.5 log10 IU/mL) independent of HBeAg status.
Conclusions: RO7062931 is safe and well tolerated at doses up to 4.0 mg/kg QW. Supradose-proportional exposure at doses of 3.0-4.0 mg/kg was indicative of partial saturation of the ASGPR-mediated liver uptake system. Dose-dependent declines in HBsAg demonstrated target engagement with RO7062931.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03038113.
© 2021 Roche Products Ltd. Hepatology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Figures
Comment in
-
Letter to the Editor: Is the HBsAg response to RO7062931 an antisense effect?Hepatology. 2022 Jan;75(1):230-231. doi: 10.1002/hep.32103. Epub 2021 Nov 27. Hepatology. 2022. PMID: 34387887 No abstract available.
-
Reply.Hepatology. 2022 Apr;75(4):1050-1051. doi: 10.1002/hep.32113. Epub 2021 Dec 13. Hepatology. 2022. PMID: 34396570 No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organization . Global hepatitis report 2017. https://www/who.int/publications/i/item/global‐hepatitis‐report‐2017. Accessed September 16, 2020.
-
- Yuen MF, Chen DS, Dusheiko GM, Janssen HL, Lau DT, Locarnini SA, et al. Hepatitis B virus infection. Nat Rev Dis Primer 2018;4:18035. - PubMed
-
- Anderson RT, Choi HS, Lenz O, Peters MG, Janssen HL, Mishra P, et al. Association between seroclearance of hepatitis B surface antigen and long‐term clinical outcomes of patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection: systematic review and meta‐analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2021;19:463‐472. - PubMed
-
- European Association for the Study of the Liver . EASL 2017 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol 2017;67:370‐398. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

