Ustekinumab in Paediatric Patients with Moderately to Severely Active Crohn's Disease: Pharmacokinetics, Safety, and Efficacy Results from UniStar, a Phase 1 Study
- PMID: 34037715
- PMCID: PMC8575045
- DOI: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjab089
Ustekinumab in Paediatric Patients with Moderately to Severely Active Crohn's Disease: Pharmacokinetics, Safety, and Efficacy Results from UniStar, a Phase 1 Study
Abstract
Background and aims: The objective was to evaluate the pharmacokinetics, safety/tolerability, and efficacy of ustekinumab in children with moderately to severely active Crohn's disease.
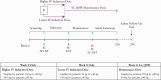
Methods: In this Phase 1, multicentre, 16-week, double-blind, induction dose-ranging study [NCT02968108], patients aged 2-<18 years [body weight ≥10 kg] were randomised [1:1] to one of two weight range-based intravenous induction doses: 130 mg vs 390 mg in patients ≥40kg and 3 mg/kg vs 9 mg/kg in patients <40kg. At Week 8, all patients received a single subcutaneous ustekinumab maintenance dose of 90 mg in patients ≥40kg or 2 mg/kg in patients <40kg.
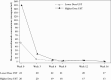
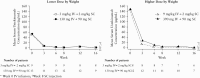
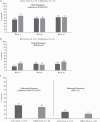
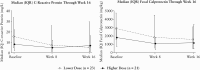
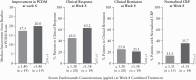
Results: A total of 44 patients were randomised and treated with ustekinumab [n = 23 lower dose; n = 21 higher dose]; median [interquartile range] age was 13.0 [12-16] years. Pharmacokinetics were similar to those in adults with Crohn's disease. However, serum ustekinumab concentrations were lower among those with body weight <40 kg compared with patients ≥40 kg and the reference Phase 3 adult population. Through Week 16, 73% of patients reported ≥1 adverse event [82.6% lower vs 62% higher dose]; two discontinued due to adverse events [one in each group]. Serious adverse events occurred in 16% [26% lower, 5% higher dose], with Crohn's disease exacerbation being the most frequent. At Week 16, 22%/29% [lower/higher dose] achieved clinical remission [Paediatric Crohn's Disease Activity Index ≤10].
Conclusions: The pharmacokinetics/safety profiles were generally consistent with those observed in adults with Crohn's disease. These results suggest a different dosing regimen may be required for patients <40 kg from that employed in this study; additional pharmacokinetic analyses may be needed in this population.
Keywords: Crohn’s disease; paediatric; ustekinumab.
© European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation 2021.
Figures



References
-
- Fumery M, Pariente B, Sarter H, et al. ; Epimad Group. Long-term outcome of pediatric-onset Crohn’s disease: a population-based cohort study. Dig Liver Dis 2019;51:496–502. - PubMed
-
- Vernier-Massouille G, Balde M, Salleron J, et al. . Natural history of pediatric Crohn’s disease: a population-based cohort study. Gastroenterology 2008;135:1106–13. - PubMed
-
- Assa A, Hartman C, Weiss B, et al. . Long-term outcome of tumour necrosis factor alpha antagonist treatment in paediatric Crohn’s disease. J Crohns Colitis 2013;7:369–76. - PubMed
-
- Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies. STELARA [ustekinumab] [package insert] .High Wycombe, UK: Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies; 2020.].
-
- Feagan BG, Sandborn WJ, Gasink C, et al. ; UNITI–IM-UNITI Study Group. Ustekinumab as induction and maintenance therapy for Crohn’s disease. N Engl J Med 2016;375:1946–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

