The Role of Electronic Health Records in Advancing Genomic Medicine
- PMID: 34038146
- PMCID: PMC9297710
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-genom-121120-125204
The Role of Electronic Health Records in Advancing Genomic Medicine
Abstract
Recent advances in genomic technology and widespread adoption of electronic health records (EHRs) have accelerated the development of genomic medicine, bringing promising research findings from genome science into clinical practice. Genomic and phenomic data, accrued across large populations through biobanks linked to EHRs, have enabled the study of genetic variation at a phenome-wide scale. Through new quantitative techniques, pleiotropy can be explored with phenome-wide association studies, the occurrence of common complex diseases can be predicted using the cumulative influence of many genetic variants (polygenic risk scores), and undiagnosed Mendelian syndromes can be identified using EHR-based phenotypic signatures (phenotype risk scores). In this review, we trace the role of EHRs from the development of genome-wide analytic techniques to translational efforts to test these new interventions to the clinic. Throughout, we describe the challenges that remain when combining EHRs with genetics to improve clinical care.
Keywords: GWAS; PheRS; PheWAS; electronic health records; phenome; translational genomics.
Figures
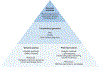
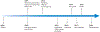

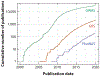
References
LITERATURE CITED
-
- Abul-Husn NS, Manickam K, Jones LK, Wright EA, Hartzel DN, et al. 2016. Genetic identification of familial hypercholesterolemia within a single U.S. health care system. Science 354:aaf7000. - PubMed
-
- Adler-Milstein J, Jha AK. 2017. HITECH Act drove large gains in hospital electronic health record adoption. Health Aff. 36:1416–22 - PubMed
RELATED RESOURCES
-
- Clinical Trials.gov: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov
-
- Electronic Medical Records and Genomics (eMERGE) network: https://emerge-network.org
-
- GWAS Catalog: https://www.ebi.ac.uk/gwas
-
- Informatics for Integrating Biology and the Bedside (i2b2): https://www.i2b2.org
-
- National COVID Cohort Collaborative: https://covid.cd2h.org
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

