Amphiphilic Iodine(III) Reagents for the Lipophilization of Peptides in Water
- PMID: 34038604
- PMCID: PMC8456932
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.202106458
Amphiphilic Iodine(III) Reagents for the Lipophilization of Peptides in Water
Abstract
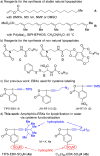
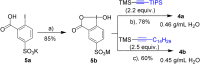
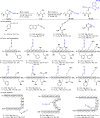
We report the functionalization of cysteine residues with lipophilic alkynes bearing a silyl group or an alkyl chain using amphiphilic ethynylbenziodoxolone reagents (EBXs). The reactions were carried out in buffer (pH 6 to 9), without organic co-solvent or removal of oxygen, either at 37 °C or room temperature. The transformation led to a significant increase of peptide lipophilicity and worked for aromatic thiols, homocysteine, cysteine, and peptides containing 4 to 18 amino acids. His6 -Cys-Ubiquitin was also alkynylated under physiological conditions. Under acidic conditions, the thioalkynes were converted into thioesters, which could be cleaved in the presence of hydroxylamine.
Keywords: amphiphilic reagents; hypervalent iodine; lipidation; lipopeptide; ubiquitin.
© 2021 The Authors. Angewandte Chemie International Edition published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
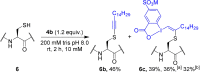

References
-
- None
-
- Castanho M., Santos N. C., Peptide Drug Discovery and Development, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2011;
-
- Craik D. J., Fairlie D. P., Liras S., Price D., Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2013, 81, 136; - PubMed
-
- Dunn B. M., Peptide Chemistry and Drug Design, Wiley, Hoboken, 2015;
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

