Pediatric Lipid Disorders
- PMID: 34038650
- PMCID: PMC8544611
- DOI: 10.3928/19382359-20210218-01
Pediatric Lipid Disorders
Abstract
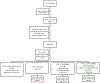
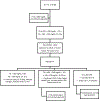
Current scientific evidence has proven that atherosclerosis is a process that begins in childhood and tracks into adulthood, likely culminating in adverse cardiovascular events such as coronary artery disease, peripheral artery disease, and stroke. In addition, the obesity epidemic and increasing awareness of genetic lipid disorders has made the understanding and management of lipid disorders necessary for pediatricians. Childhood offers a unique opportunity for preventing, modifying, or eliminating risk factors and, in doing so, reversing or slowing the process of atherosclerosis. In general, management involves targeted lifestyle interventions such as strict dietary changes and increases in physical activity. In some circumstances, pharmacotherapy, even in childhood, is warranted. [Pediatr Ann. 2021;50(3):e105-e112.].
Figures
Similar articles
-
Primary and secondary disorders of lipid metabolism in pediatrics.Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2008 Feb;5 Suppl 2:727-38. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2008. PMID: 18317444 Review.
-
The effect of weight management interventions that include a diet component on weight-related outcomes in pregnant and postpartum women: a systematic review protocol.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015 Jan;13(1):88-98. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2015-1812. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015. PMID: 26447010
-
JCL roundtable: Pediatric lipidology.J Clin Lipidol. 2019 Sep-Oct;13(5):676-688. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2019.10.010. J Clin Lipidol. 2019. PMID: 31783974
-
Management of Obesity and Its Complications in Children and Adolescents.Indian J Pediatr. 2021 Dec;88(12):1222-1234. doi: 10.1007/s12098-021-03913-3. Epub 2021 Oct 5. Indian J Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34609654 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification, evaluation, and management of obesity in an academic primary care center.Pediatrics. 2004 Aug;114(2):e154-9. doi: 10.1542/peds.114.2.e154. Pediatrics. 2004. PMID: 15286251
Cited by
-
Dyslipidemia in Pediatric Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Aug 8;59(8):1434. doi: 10.3390/medicina59081434. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 37629724 Free PMC article.
-
Transitioning Adolescents and Young Adults with Lipid Disorders to Adult Health Care.Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2024 Dec;26(12):693-700. doi: 10.1007/s11883-024-01244-0. Epub 2024 Oct 2. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2024. PMID: 39356422 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Benjamin J, Muntner S, Alonso W, et al. (2019) Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics—2019 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 139:e56–e66 - PubMed
-
- Ford ES, Ajani UA, Croft JB, Critchley JA, Labarthe DR, Kottke TE, Giles WH, Capewell S (2007) Explaining the Decrease in U.S. Deaths from Coronary Disease, 1980–2000. N Engl J Med 356:2388–2398 - PubMed
-
- Enos WF, Holmes RH, Beyer J (1953) Coronary disease among United States soldiers killed in action in Korea; preliminary report. J Am Med Assoc 152:1090–1093 - PubMed
-
- McNamara JJ, Molot MA, Stremple JF, Cutting RT (1971) Coronary artery disease in combat casualties in Vietnam. JAMA 216:1185–1187 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

