Safety and efficacy profile of mogamulizumab (Poteligeo) in the treatment of cancers: an update evidence from 14 studies
- PMID: 34039310
- PMCID: PMC8157723
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-021-08363-w
Safety and efficacy profile of mogamulizumab (Poteligeo) in the treatment of cancers: an update evidence from 14 studies
Abstract
Background: CC chemokine receptor 4 (CCR4), the receptor for CCL22 and CCL17, is expressed on the surface of effector Tregs that have the highest suppressive effects on antitumor immune response. CCR4 is also widely expressed on the surface of tumor cells from patients with adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATL), peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL) and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL). Mogamulizumab is a humanized, IgG1 kappa monoclonal antibody that is directed against CCR4. By reducing the number of CCR4-positive Tregs and tumor cells, the mogamulizumab can reduce tumor burden and boost antitumor immunity to achieve antitumor effects.
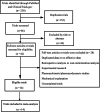
Methods: We examined the PubMed and ClinicalTrials.gov until 1 February 2020. Considering variability in different studies, we selected the adverse events (AEs), overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), objective responses rate (ORR) and Hazard Ratio (HR) for PFS to evaluate the safety and efficacy profile of mogamulizumab.
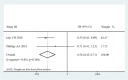
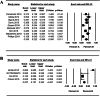
Results: When patients were treated with mogamulizumab monotherapy, the most common all-grade AEs were lymphopenia, infusion reaction, fever, rash and chills while the most common grade ≥ 3 AEs were lymphopenia, neutropenia and rash. When patients were treated with combined therapy of mogamulizumab and other drugs, the most common all-grade AEs were neutropenia, anaemia, lymphopenia and gastrointestinal disorder, while the most common grade ≥ 3 AEs was lymphopenia. For patients treated with mogamulizumab monotherapy, the pooled ORR and mean PFS were 0.430 (95% CI: 0.393-0.469) and 1.060 months (95% CI: 1.043-1.077), respectively. For patients treated with combined therapy of mogamulizumab and other drugs, the pooled ORR was 0.203 (95% CI: 0.022-0.746) while the pooled PFS and OS were 2.093 months (95% CI: 1.602-2.584) and 6.591 months (95% CI: 6.014-7.167), respectively.
Conclusions: Based on present evidence, we believed that mogamulizumab had clinically meaningful antitumor activity with acceptable toxicity which is a novel therapy in treating patients with cancers.
Keywords: CCR4; Malignant lymphoma; Meta-analysis; Mogamulizumab; Solid tumors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Multicenter phase II study of mogamulizumab (KW-0761), a defucosylated anti-cc chemokine receptor 4 antibody, in patients with relapsed peripheral T-cell lymphoma and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.J Clin Oncol. 2014 Apr 10;32(11):1157-63. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2013.52.0924. Epub 2014 Mar 10. J Clin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24616310 Clinical Trial.
-
A Phase I Study of the Anti-CC Chemokine Receptor 4 Antibody, Mogamulizumab, in Combination with Nivolumab in Patients with Advanced or Metastatic Solid Tumors.Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Nov 15;25(22):6614-6622. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-1090. Epub 2019 Aug 27. Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31455681 Clinical Trial.
-
Safety and effectiveness of mogamulizumab in relapsed or refractory CC chemokine receptor 4-positive peripheral T-cell lymphoma and relapsed or refractory cutaneous T-cell lymphoma: A post-marketing surveillance in Japan.Hematol Oncol. 2024 Jul;42(4):e3292. doi: 10.1002/hon.3292. Hematol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38847317
-
Mogamulizumab: An Anti-CC Chemokine Receptor 4 Antibody for T-Cell Lymphomas.Ann Pharmacother. 2020 Apr;54(4):371-379. doi: 10.1177/1060028019884863. Epub 2019 Oct 25. Ann Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 31648540 Review.
-
Mogamulizumab and the treatment of CCR4-positive T-cell lymphomas.Immunotherapy. 2014;6(11):1187-206. doi: 10.2217/imt.14.94. Immunotherapy. 2014. PMID: 25496334 Review.
Cited by
-
Trametinib improves Treg selectivity of anti-CCR4 antibody by regulating CCR4 expression in CTLs in oral squamous cell carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2022 Dec 15;12(1):21678. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-22773-1. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36522365 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Mogamulizumab in Real-Life Advanced Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphomas: A Multicentric Retrospective Cohort Study.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Mar 25;14(7):1659. doi: 10.3390/cancers14071659. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35406431 Free PMC article.
-
CCR4 as a Therapeutic Target for Cancer Immunotherapy.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Nov 4;13(21):5542. doi: 10.3390/cancers13215542. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34771703 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quality of Life in Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma Patients Receiving Mogamulizumab: Important Factors to Consider.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Dec 21;15(1):32. doi: 10.3390/cancers15010032. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36612028 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the role of chemokines in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma: expression levels at different stages.Front Immunol. 2025 Aug 8;16:1646669. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1646669. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40861461 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yoshie O, Matsushima KJII. CCR4 and its ligands: from bench to bedside. Int immun. 2015;27(1):11–20. - PubMed
-
- Sokolowska-Wojdylo M, Wenzel J, Gaffal E, Lenz J, TTJBJo D. Circulating clonal CLA+ and CD4+ T cells in Sézary syndrome express the skin-homing chemokine receptors CCR4 and CCR10 as well as the lymph node-homing chemokine receptor CCR7. Br J Dermatol 2005;152(2):258–64. - PubMed
-
- Susumu S, Takashi, Ishida, Kazuhiro, Yoshikawa, Ryuzo . Oncology UJJJoC: Current status of immunotherapy. 2016. - PubMed
-
- Ferenczi K, Fuhlbrigge RC, Pinkus J, Pinkus GS, Kupper TS. Increased CCR4 expression in cutaneous T cell lymphoma. J invest Dermatol 2002;119(6):1405–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

