Exosomal DLX6-AS1 from hepatocellular carcinoma cells induces M2 macrophage polarization to promote migration and invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma through microRNA-15a-5p/CXCL17 axis
- PMID: 34039401
- PMCID: PMC8152341
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-021-01973-z
Exosomal DLX6-AS1 from hepatocellular carcinoma cells induces M2 macrophage polarization to promote migration and invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma through microRNA-15a-5p/CXCL17 axis
Retraction in
-
Retraction Note: Exosomal DLX6-AS1 from hepatocellular carcinoma cells induces M2 macrophage polarization to promote migration and invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma through microRNA-15a-5p/CXCL17 axis.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Apr 9;41(1):134. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02353-x. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35395944 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells-secreted exosomes (exo) could stimulate M2 macrophage polarization and promote HCC progression, but the related mechanism of long non-coding RNA distal-less homeobox 6 antisense 1 (DLX6-AS1) with HCC-exo-mediated M2 macrophage polarization is largely ambiguous. Thereafter, this research was started to unearth the role of DLX6-AS1 in HCC-exo in HCC through M2 macrophage polarization and microRNA (miR)-15a-5p/C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 17 (CXCL17) axis.
Methods: DLX6-AS1, miR-15a-5p and CXCL17 expression in HCC tissues and cells were tested. Exosomes were isolated from HCC cells with overexpressed DLX6-AS1 and co-cultured with M2 macrophages. MiR-15a-5p/CXCL17 down-regulation assays were performed in macrophages. The treated M2 macrophages were co-cultured with HCC cells, after which cell migration, invasion and epithelial mesenchymal transition were examined. The targeting relationships between DLX6-AS1 and miR-15a-5p, and between miR-15a-5p and CXCL17 were explored. In vivo experiment was conducted to detect the effect of exosomal DLX6-AS1-induced M2 macrophage polarization on HCC metastasis.
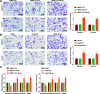
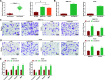
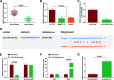
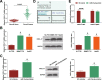
Results: Promoted DLX6-AS1 and CXCL17 and reduced miR-15a-5p exhibited in HCC. HCC-exo induced M2 macrophage polarization to accelerate migration, invasion and epithelial mesenchymal transition in HCC, which was further enhanced by up-regulated DLX6-AS1 but impaired by silenced DLX6-AS1. Inhibition of miR-15a-5p promoted M2 macrophage polarization to stimulate the invasion and metastasis of HCC while that of CXCL17 had the opposite effects. DLX6-AS1 mediated miR-15a-5p to target CXCL17. DLX6-AS1 from HCC-exo promoted metastasis in the lung by inducing M2 macrophage polarization in vivo.
Conclusion: DLX6-AS1 from HCC-exo regulates CXCL17 by competitively binding to miR-15a-5p to induce M2 macrophage polarization, thus promoting HCC migration, invasion and EMT.
Keywords: C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 17; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Hepatocellular carcinoma cell-secreted exosomes; Long non-coding RNA distal-less homeobox 6 antisense 1; M2 macrophages; microRNA-15a-5p.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Advances and challenges of exosome-derived noncoding RNAs for hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis and treatment.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2024 Mar 24;38:101695. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2024.101695. eCollection 2024 Jul. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2024. PMID: 38560049 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomal miR-452-5p Induce M2 Macrophage Polarization to Accelerate Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression by Targeting TIMP3.J Immunol Res. 2022 Sep 16;2022:1032106. doi: 10.1155/2022/1032106. eCollection 2022. J Immunol Res. 2022. PMID: 36164322 Free PMC article.
-
Long noncoding RNA DLX6-AS1 promotes liver cancer by increasing the expression of WEE1 via targeting miR-424-5p.J Cell Biochem. 2019 Aug;120(8):12290-12299. doi: 10.1002/jcb.28493. Epub 2019 Feb 25. J Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30805988 Free PMC article.
-
miR-660-5p-loaded M2 macrophages-derived exosomes augment hepatocellular carcinoma development through regulating KLF3.Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Dec;101(Pt B):108157. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108157. Epub 2021 Oct 18. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34673296
-
MicroRNA as Key Players in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Insights into Their Role in Metastasis.Biochem Genet. 2025 Apr;63(2):1014-1062. doi: 10.1007/s10528-024-10897-0. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Biochem Genet. 2025. PMID: 39103713 Review.
Cited by
-
Roles and mechanisms of exosomal non-coding RNAs in human health and diseases.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021 Nov 10;6(1):383. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00779-x. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021. PMID: 34753929 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Long Non-Coding RNA and microRNA Networks in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Its Tumor Microenvironment.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 30;22(19):10630. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910630. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34638971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PCMT1 is a potential target related to tumor progression and immune infiltration in liver cancer.Eur J Med Res. 2023 Aug 18;28(1):289. doi: 10.1186/s40001-023-01216-1. Eur J Med Res. 2023. PMID: 37596654 Free PMC article.
-
Non-coding RNA-associated competitive endogenous RNA regulatory networks: Novel diagnostic and therapeutic opportunities for hepatocellular carcinoma.J Cell Mol Med. 2022 Jan;26(2):287-305. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17126. Epub 2021 Dec 14. J Cell Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 34907642 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances and challenges of exosome-derived noncoding RNAs for hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis and treatment.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2024 Mar 24;38:101695. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2024.101695. eCollection 2024 Jul. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2024. PMID: 38560049 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

