Single-Dose Pembrolizumab Treatment for Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy
- PMID: 34039733
- PMCID: PMC8159157
- DOI: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000001021
Single-Dose Pembrolizumab Treatment for Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy
Figures
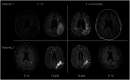
References
-
- Cortese I, Muranski P, Enose-Akahata Y, et al. . Pembrolizumab treatment for progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(17):1597-1605. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
