Cytokine expression patterns in hospitalized children with Bordetella pertussis, Rhinovirus or co-infection
- PMID: 34040002
- PMCID: PMC8154898
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-89538-0
Cytokine expression patterns in hospitalized children with Bordetella pertussis, Rhinovirus or co-infection
Abstract
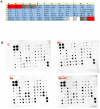
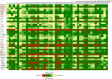
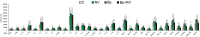
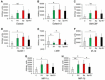
Mechanisms of interaction between Bordetella pertussis and other viral agents are yet to be fully explored. We studied the inflammatory cytokine expression patterns among children with both viral-bacterial infections. Nasopharyngeal aspirate (NPA) samples were taken from children, aged < 1 year, positive for Rhinovirus, Bordetella pertussis and for Rhinovirus and Bordetella pertussis. Forty cytokines were evaluated in NPA by using human cytokine protein arrays and a quantitative analysis was performed on significantly altered cytokines. Forty cytokines were evaluated in NPA by using human cytokine protein arrays and a quantitative analysis was performed on significantly altered cytokines. Our results show that co-infections display a different inflammatory pattern compared to single infections, suggesting that a chronic inflammation caused by one of the two pathogens could be the trigger for exacerbation in co-infections.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nasopharyngeal microbiota in hospitalized children with Bordetella pertussis and Rhinovirus infection.Sci Rep. 2021 Nov 24;11(1):22858. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-02322-y. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34819600 Free PMC article.
-
Allergic environment enhances airway epithelial pro-inflammatory responses to rhinovirus infection.Clin Sci (Lond). 2017 Mar 1;131(6):499-509. doi: 10.1042/CS20160939. Epub 2017 Jan 23. Clin Sci (Lond). 2017. PMID: 28115681
-
Bordetella pertussis and concomitant viral respiratory tract infections are rare in children with cough illness.Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2011 Aug;30(8):640-4. doi: 10.1097/INF.0b013e3182152d28. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2011. PMID: 21407144
-
Epidemiology of pertussis in Casablanca (Morocco): contribution of conventional and molecular diagnosis tools.BMC Infect Dis. 2017 May 16;17(1):348. doi: 10.1186/s12879-017-2452-3. BMC Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 28511667 Free PMC article.
-
Pertussis in the newborn: certainties and uncertainties in 2014.Paediatr Respir Rev. 2015 Mar;16(2):112-8. doi: 10.1016/j.prrv.2014.01.004. Epub 2014 Jan 31. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2015. PMID: 25613084 Review.
Cited by
-
Nasopharyngeal microbiota in hospitalized children with Bordetella pertussis and Rhinovirus infection.Sci Rep. 2021 Nov 24;11(1):22858. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-02322-y. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34819600 Free PMC article.
-
Respiratory Viral Coinfections: Insights into Epidemiology, Immune Response, Pathology, and Clinical Outcomes.Pathogens. 2024 Apr 12;13(4):316. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13040316. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 38668271 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nieves DJ, Heininger U. Bordetella pertussis. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016;4(3):110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

