Cytokine expression patterns in hospitalized children with Bordetella pertussis, Rhinovirus or co-infection
- PMID: 34040002
- PMCID: PMC8154898
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-89538-0
Cytokine expression patterns in hospitalized children with Bordetella pertussis, Rhinovirus or co-infection
Abstract
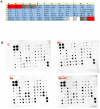
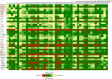
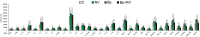
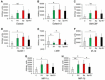
Mechanisms of interaction between Bordetella pertussis and other viral agents are yet to be fully explored. We studied the inflammatory cytokine expression patterns among children with both viral-bacterial infections. Nasopharyngeal aspirate (NPA) samples were taken from children, aged < 1 year, positive for Rhinovirus, Bordetella pertussis and for Rhinovirus and Bordetella pertussis. Forty cytokines were evaluated in NPA by using human cytokine protein arrays and a quantitative analysis was performed on significantly altered cytokines. Forty cytokines were evaluated in NPA by using human cytokine protein arrays and a quantitative analysis was performed on significantly altered cytokines. Our results show that co-infections display a different inflammatory pattern compared to single infections, suggesting that a chronic inflammation caused by one of the two pathogens could be the trigger for exacerbation in co-infections.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Nieves DJ, Heininger U. Bordetella pertussis. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016;4(3):110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

