Sensorineural hearing loss and risk of stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 34040004
- PMCID: PMC8155183
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-89695-2
Sensorineural hearing loss and risk of stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
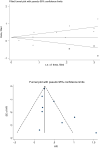
The aim of this systematic review and meta-analysis study was to clarify the effects of sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) on the incidence of stroke. In line with this, PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and ScienceDirect databases were searched using related keywords and MeSH terms from inception to March 1, 2020. Out of the 1961 initial records, eight cohort studies comprising 4,564,202 participants were included, and their qualities were assessed using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS). Then, the random-effects model was used to pool HR (95% CI) for risk of stroke; and heterogeneity was presented with I2 index. Subgroup analysis and publication bias tests were performed, and the pooled HR (95% CI) of stroke in SNHL was estimated as 1.31 (1.08, 1.53) for the unadjusted model and 1.33 (1.18, 1.49) for the adjusted model. Subgroup analysis indicates a significantly higher risk of stroke in patients with sudden SNHL (SSNHL) in comparison to age-related HL (ARHL) both in the unadjusted model, [HR = 1.46; 95% CI (1.08, 1.63)] versus [HR = 1.14; 95% CI (0.64, 1.65)], and in the adjusted model, [HR = 1.44; 95% CI (1.15, 1.74)] versus [HR = 1.29; 95% CI (1.24, 1.34)]. Our study showed that patients with SNHL face a higher risk of stroke than those without SNHL. It is necessary to perform hematologic and neurological examinations to help clinicians detect patients who are potentially at risk for stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Sensorineural hearing loss in stroke: an age-matched retrospective study.J Laryngol Otol. 2025 Jan;139(1):19-22. doi: 10.1017/S0022215124001051. Epub 2025 Jan 3. J Laryngol Otol. 2025. PMID: 39748781
-
Risk of sudden sensorineural hearing loss in stroke patients: A 5-year nationwide investigation of 44,460 patients.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Sep;95(36):e4841. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000004841. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 27603402 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of the relationship between sensorineural hearing loss and associated comorbidities in patients with chronic kidney disease: A nationwide, population-based cohort study.PLoS One. 2020 Sep 11;15(9):e0238913. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0238913. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32915865 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Alopecia Areata with Sensorineural Hearing Loss: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Dermatology. 2023;239(4):523-532. doi: 10.1159/000530784. Epub 2023 Apr 24. Dermatology. 2023. PMID: 37094565 Free PMC article.
-
Risk of Stroke and Myocardial Infarction After Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: A Meta-Analysis.Laryngoscope. 2021 Jun;131(6):1369-1377. doi: 10.1002/lary.29237. Epub 2020 Nov 6. Laryngoscope. 2021. PMID: 33156954
Cited by
-
Vertebrobasilar System Laterality and Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss.Audiol Neurootol. 2024;29(2):114-123. doi: 10.1159/000534153. Epub 2023 Oct 20. Audiol Neurootol. 2024. PMID: 37866348 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory diet, gut microbiota and sensorineural hearing loss: a cross-sectional and Mendelian randomization study.Front Nutr. 2024 Aug 16;11:1458484. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1458484. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39221159 Free PMC article.
-
Update on Findings about Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss and Insight into Its Pathogenesis.J Clin Med. 2022 Oct 28;11(21):6387. doi: 10.3390/jcm11216387. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36362614 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Challenge of Diagnosing Labyrinthine Stroke-A Critical Review.Brain Sci. 2025 Jul 7;15(7):725. doi: 10.3390/brainsci15070725. Brain Sci. 2025. PMID: 40722316 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early detection of stroke at the sudden sensorineural hearing loss stage.Front Neurol. 2023 Nov 1;14:1293102. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1293102. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 38020605 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zazove P, Atcherson SR, Moreland C, McKee MM. Hearing loss: Diagnosis and evaluation. FP essentials. 2015;434:11–17. - PubMed
-
- Word Health Organization. Deafness and hearing loss (2019).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

