EGCG promotes PRKCA expression to alleviate LPS-induced acute lung injury and inflammatory response
- PMID: 34040072
- PMCID: PMC8154949
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-90398-x
EGCG promotes PRKCA expression to alleviate LPS-induced acute lung injury and inflammatory response
Abstract
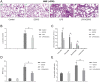
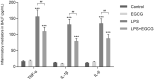
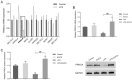
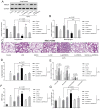
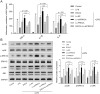
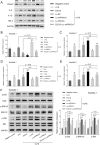
Acute lung injury (ALI), which could be induced by multiple factors such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS), refer to clinical symptoms of acute respiratory failure, commonly with high morbidity and mortality. Reportedly, active ingredients from green tea have anti-inflammatory and anticancer properties, including epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG). In the present study, protein kinase C alpha (PRKCA) is involved in EGCG protection against LPS-induced inflammation and ALI. EGCG treatment attenuated LPS-stimulated ALI in mice as manifested as improved lung injury scores, decreased total cell amounts, neutrophil amounts and macrophage amounts, inhibited the activity of MPO, decreased wet-to-dry weight ratio of lung tissues, and inhibited release of inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6. PRKCA mRNA and protein expression showed to be dramatically decreased by LPS treatment while reversed by EGCG treatment. Within LPS-stimulated ALI mice, PRKCA silencing further aggravated, while PRKCA overexpression attenuated LPS-stimulated inflammation and ALI through MAPK signaling pathway. PRKCA silencing attenuated EGCG protection. Within LPS-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages, EGCG could induce PRKCA expression. Single EGCG treatment or Lv-PRKCA infection attenuated LPS-induced increases in inflammatory factors; PRKCA silencing could reverse the suppressive effects of EGCG upon LPS-stimulated inflammatory factor release. In conclusion, EGCG pretreatment inhibits LPS-induced ALI in mice. The protective mechanism might be associated with the inhibitory effects of PRKCA on proinflammatory cytokine release via macrophages and MAPK signaling pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG), an Active Compound of Green Tea Attenuates Acute Lung Injury Regulating Macrophage Polarization and Krüpple-Like-Factor 4 (KLF4) Expression.Molecules. 2020 Jun 20;25(12):2853. doi: 10.3390/molecules25122853. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32575718 Free PMC article.
-
Dehydrocostus Lactone Suppresses LPS-induced Acute Lung Injury and Macrophage Activation through NF-κB Signaling Pathway Mediated by p38 MAPK and Akt.Molecules. 2019 Apr 17;24(8):1510. doi: 10.3390/molecules24081510. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 30999647 Free PMC article.
-
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by suppression of TLR4/NF-κB signaling activation.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2019;52(7):e8092. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X20198092. Epub 2019 Jun 19. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2019. PMID: 31241712 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular hydrogen ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice through reducing inflammation and apoptosis.Shock. 2012 May;37(5):548-55. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0b013e31824ddc81. Shock. 2012. PMID: 22508291
-
Syringic acid attenuates acute lung injury by modulating macrophage polarization in LPS-induced mice.Phytomedicine. 2024 Jul;129:155591. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155591. Epub 2024 Apr 15. Phytomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38692075
Cited by
-
Recent Progress in Research on Mechanisms of Action of Natural Products against Alzheimer's Disease: Dietary Plant Polyphenols.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 11;23(22):13886. doi: 10.3390/ijms232213886. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430365 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PRKCA Promotes Mitophagy through the miR-15a-5p/PDK4 Axis to Relieve Sepsis-Induced Acute Lung Injury.Infect Immun. 2023 Jan 24;91(1):e0046522. doi: 10.1128/iai.00465-22. Epub 2022 Nov 30. Infect Immun. 2023. PMID: 36448837 Free PMC article.
-
Combination therapy with budesonide and N-acetylcysteine ameliorates LPS-induced ALI by attenuating neutrophil recruitment through the miR-196b-5p/Socs3 molecular axis.BMC Pulm Med. 2022 Oct 26;22(1):388. doi: 10.1186/s12890-022-02185-7. BMC Pulm Med. 2022. PMID: 36289489 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell sequencing combined with machine learning reveals the mechanism of interaction between epilepsy and stress cardiomyopathy.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 27;14:1078731. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1078731. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36776884 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomics Combined with Network Pharmacology-Based Strategy to Reveal the Underlying Mechanism of Zhenhuang Submicron Emulsion in Treating Oropharyngeal Mucositis Complications of Radiation Therapy for Head and Neck Cancer.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022 Sep 17;16:3169-3182. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S376984. eCollection 2022. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022. PMID: 36158237 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

