Preclinical and clinical characterization of the RORγt inhibitor JNJ-61803534
- PMID: 34040108
- PMCID: PMC8155022
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-90497-9
Preclinical and clinical characterization of the RORγt inhibitor JNJ-61803534
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Preclinical and clinical characterization of the RORγt inhibitor JNJ-61803534.Sci Rep. 2022 Apr 6;12(1):5740. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-09558-2. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35388049 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
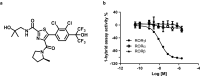
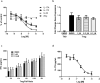
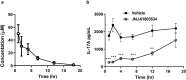
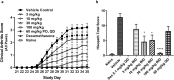
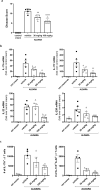
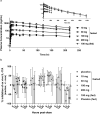
The nuclear receptor retinoid-related orphan receptor gamma t (RORγt) plays a critical role in driving Th17 cell differentiation and expansion, as well as IL-17 production in innate and adaptive immune cells. The IL-23/IL-17 axis is implicated in several autoimmune and inflammatory diseases, and biologics targeting IL-23 and IL-17 have shown significant clinical efficacy in treating psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. JNJ-61803534 is a potent RORγt inverse agonist, selectively inhibiting RORγt-driven transcription versus closely-related family members, RORα and RORβ. JNJ-61803534 inhibited IL-17A production in human CD4+ T cells under Th17 differentiation conditions, but did not inhibit IFNγ production under Th1 differentiation conditions, and had no impact on in vitro differentiation of regulatory T cells (Treg), nor on the suppressive activity of natural Tregs. In the mouse collagen-induced arthritis model, JNJ-61803534 dose-dependently attenuated inflammation, achieving ~ 90% maximum inhibition of clinical score. JNJ-61803534 significantly inhibited disease score in the imiquimod-induced mouse skin inflammation model, and dose-dependently inhibited the expression of RORγt-regulated genes, including IL-17A, IL-17F, IL-22 and IL-23R. Preclinical 1-month toxicity studies in rats and dogs identified doses that were well tolerated supporting progression into first-in-human studies. An oral formulation of JNJ-61803534 was studied in a phase 1 randomized double-blind study in healthy human volunteers to assess safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics. The compound was well tolerated in single ascending doses (SAD) up to 200 mg, and exhibited dose-dependent increases in exposure upon oral dosing, with a plasma half-life of 164 to 170 h. In addition, dose-dependent inhibition of ex vivo stimulated IL-17A production in whole blood was observed, demonstrating in vivo target engagement. In conclusion, JNJ-61803534 is a potent and selective RORγt inhibitor that exhibited acceptable preclinical safety and efficacy, as well as an acceptable safety profile in a healthy volunteer SAD study, with clear evidence of a pharmacodynamic effect in humans.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pharmacologic modulation of RORγt translates to efficacy in preclinical and translational models of psoriasis and inflammatory arthritis.Sci Rep. 2016 Dec 1;6:37977. doi: 10.1038/srep37977. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27905482 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacologic inhibition of RORγt regulates Th17 signature gene expression and suppresses cutaneous inflammation in vivo.J Immunol. 2014 Mar 15;192(6):2564-75. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1302190. Epub 2014 Feb 10. J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24516202
-
Antagonizing Retinoic Acid-Related-Orphan Receptor Gamma Activity Blocks the T Helper 17/Interleukin-17 Pathway Leading to Attenuated Pro-inflammatory Human Keratinocyte and Skin Responses.Front Immunol. 2019 Mar 26;10:577. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00577. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30972071 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription Factor Retinoid-Related Orphan Receptor γt: A Promising Target for the Treatment of Psoriasis.Front Immunol. 2018 May 30;9:1210. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01210. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29899748 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Th17 Cells with Small Molecules and Small Interference RNA.Mediators Inflamm. 2015;2015:290657. doi: 10.1155/2015/290657. Epub 2015 Dec 17. Mediators Inflamm. 2015. PMID: 26792955 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An inhibitor of RORγ for chronic pulmonary obstructive disease treatment.Sci Rep. 2022 May 24;12(1):8744. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-12251-z. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35610240 Free PMC article.
-
Leveraging Exosomes as the Next-Generation Bio-Shuttles: The Next Biggest Approach against Th17 Cell Catastrophe.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 21;24(8):7647. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087647. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108809 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Macrocyclic Retinoic Acid Receptor-Related Orphan Receptor C2 Inverse Agonists.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2023 Jan 18;14(2):191-198. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.2c00500. eCollection 2023 Feb 9. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2023. PMID: 36793423 Free PMC article.
-
The Interleukine-17 Cytokine Family: Role in Development and Progression of Spondyloarthritis, Current and Potential Therapeutic Inhibitors.Biomedicines. 2023 Apr 30;11(5):1328. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11051328. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37238999 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Yinxie I Formula attenuates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation via IL-23/IL-17 axis.Arch Dermatol Res. 2024 Aug 19;316(8):540. doi: 10.1007/s00403-024-03288-3. Arch Dermatol Res. 2024. PMID: 39158742 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hu X, et al. Corrigendum: Sterol metabolism controls TH17 differentiation by generating endogenous RORγ agonists. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2015;11(9):741. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

