Low-intensity ultrasound restores long-term potentiation and memory in senescent mice through pleiotropic mechanisms including NMDAR signaling
- PMID: 34040151
- PMCID: PMC8760044
- DOI: 10.1038/s41380-021-01129-7
Low-intensity ultrasound restores long-term potentiation and memory in senescent mice through pleiotropic mechanisms including NMDAR signaling
Abstract
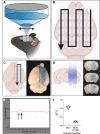
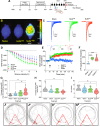
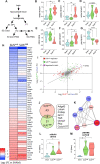
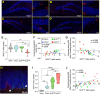
Advanced physiological aging is associated with impaired cognitive performance and the inability to induce long-term potentiation (LTP), an electrophysiological correlate of memory. Here, we demonstrate in the physiologically aged, senescent mouse brain that scanning ultrasound combined with microbubbles (SUS+MB), by transiently opening the blood-brain barrier, fully restores LTP induction in the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus. Intriguingly, SUS treatment without microbubbles (SUSonly), i.e., without the uptake of blood-borne factors, proved even more effective, not only restoring LTP, but also ameliorating the spatial learning deficits of the aged mice. This functional improvement is accompanied by an altered milieu of the aged hippocampus, including a lower density of perineuronal nets, increased neurogenesis, and synaptic signaling, which collectively results in improved spatial learning. We therefore conclude that therapeutic ultrasound is a non-invasive, pleiotropic modality that may enhance cognition in elderly humans.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Therapeutic Ultrasound as a Treatment Modality for Physiological and Pathological Ageing Including Alzheimer's Disease.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Jul 1;13(7):1002. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13071002. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34371696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ras inhibitor S-trans, trans-farnesylthiosalicylic acid enhances spatial memory and hippocampal long-term potentiation via up-regulation of NMDA receptor.Neuropharmacology. 2018 Sep 1;139:257-267. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.03.026. Epub 2018 Mar 22. Neuropharmacology. 2018. PMID: 29578035
-
Tripchlorolide improves age-associated cognitive deficits by reversing hippocampal synaptic plasticity impairment and NMDA receptor dysfunction in SAMP8 mice.Behav Brain Res. 2014 Jan 1;258:8-18. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2013.10.010. Epub 2013 Oct 17. Behav Brain Res. 2014. PMID: 24140565
-
Long-term potentiation and the role of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors.Brain Res. 2015 Sep 24;1621:5-16. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2015.01.016. Epub 2015 Jan 22. Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 25619552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hippocampal LTP modulation and glutamatergic receptors following vestibular loss.Brain Struct Funct. 2019 Mar;224(2):699-711. doi: 10.1007/s00429-018-1792-0. Epub 2018 Nov 23. Brain Struct Funct. 2019. PMID: 30470894
Cited by
-
Therapeutic ultrasound: an innovative approach for targeting neurological disorders affecting the basal ganglia.Front Neuroanat. 2024 Oct 2;18:1469250. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2024.1469250. eCollection 2024. Front Neuroanat. 2024. PMID: 39417047 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optimal timing for drug delivery into the hippocampus by focused ultrasound: A comparison of hydrophilic and lipophilic compounds.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 9;10(8):e29480. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29480. eCollection 2024 Apr 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38644896 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound and antibodies - a potentially powerful combination for Alzheimer disease therapy.Nat Rev Neurol. 2024 May;20(5):257-258. doi: 10.1038/s41582-024-00943-1. Nat Rev Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38378999 No abstract available.
-
Transcranial ultrasound stimulation parameters for neurological diseases: a systematic review.Front Neurol. 2025 May 21;16:1567482. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1567482. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40470501 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Effects of Focused Ultrasound-Induced Blood-Brain Barrier Opening on Anti-Pyroglu3 Abeta Antibody Delivery and Immune Responses.Biomolecules. 2022 Jul 6;12(7):951. doi: 10.3390/biom12070951. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35883506 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Leinenga G, Götz J. Scanning ultrasound removes amyloid-beta and restores memory in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. Sci Tran Med. 2015;7:278ra33. - PubMed
-
- Leinenga G, Langton C, Nisbet R, Götz J. Ultrasound treatment of neurological diseases—current and emerging applications. Nat Rev Neurol. 2016;12:161–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

