Early-life oxytocin attenuates the social deficits induced by caesarean-section delivery in the mouse
- PMID: 34040156
- PMCID: PMC8429532
- DOI: 10.1038/s41386-021-01040-3
Early-life oxytocin attenuates the social deficits induced by caesarean-section delivery in the mouse
Abstract
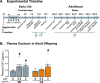
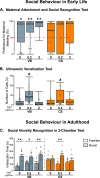
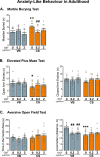
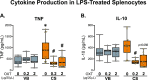
The oxytocin (OXT) system has been strongly implicated in the regulation of social behaviour and anxiety, potentially contributing to the aetiology of a wide range of neuropathologies. Birth by Caesarean-section (C-section) results in alterations in microbiota diversity in early-life, alterations in brain development and has recently been associated with long-term social and anxiety-like behaviour deficits. In this study, we assessed whether OXT intervention in the early postnatal period could reverse C-section-mediated effects on behaviour, and physiology in early life and adulthood. Following C-section or per vaginum birth, pups were administered with OXT (0.2 or 2 μg/20 μl; s.c.) or saline daily from postnatal days 1-5. We demonstrate that early postnatal OXT treatment has long-lasting effects reversing many of the effects of C-section on mouse behaviour and physiology. In early-life, high-dose OXT administration attenuated C-section-mediated maternal attachment impairments. In adulthood, low-dose OXT restored social memory deficits, some aspects of anxiety-like behaviour, and improved gastrointestinal transit. Furthermore, as a consequence of OXT intervention in early life, OXT plasma levels were increased in adulthood, and dysregulation of the immune response in C-section animals was attenuated by both doses of OXT treatment. These findings indicate that there is an early developmental window sensitive to manipulations of the OXT system that can prevent lifelong behavioural and physiological impairments associated with mode of birth.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oxytocin and vasopressin modulation of social anxiety following adolescent intermittent ethanol exposure.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2018 Oct;235(10):3065-3077. doi: 10.1007/s00213-018-5003-8. Epub 2018 Aug 23. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2018. PMID: 30141056 Free PMC article.
-
Brain oxytocin: a key regulator of emotional and social behaviours in both females and males.J Neuroendocrinol. 2008 Jun;20(6):858-65. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2826.2008.01726.x. J Neuroendocrinol. 2008. PMID: 18601710 Review.
-
Developmental Effects of Oxytocin Neurons on Social Affiliation and Processing of Social Information.J Neurosci. 2021 Oct 20;41(42):8742-8760. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2939-20.2021. Epub 2021 Sep 1. J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34470805 Free PMC article.
-
Central vasopressin and oxytocin release: regulation of complex social behaviours.Prog Brain Res. 2008;170:261-76. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)00422-6. Prog Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18655888 Review.
-
Pharmacological manipulation of oxytocin receptor signaling during mouse embryonic development results in sex-specific behavioral effects in adulthood.Horm Behav. 2021 Sep;135:105026. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2021.105026. Epub 2021 Jul 14. Horm Behav. 2021. PMID: 34273706 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Oxytocin and microglia in the development of social behaviour.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2022 Aug 29;377(1858):20210059. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2021.0059. Epub 2022 Jul 11. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35858111 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of how social memory is studied.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 26;14(1):2221. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-52277-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38278973 Free PMC article.
-
Sex, love and oxytocin: Two metaphors and a molecule.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2022 Dec;143:104948. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2022.104948. Epub 2022 Nov 5. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2022. PMID: 36347382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The oxytocin system and early-life experience-dependent plastic changes.J Neuroendocrinol. 2021 Nov;33(11):e13049. doi: 10.1111/jne.13049. Epub 2021 Oct 29. J Neuroendocrinol. 2021. PMID: 34713517 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modified neuroimmune processes and emotional behaviour in weaned and late adolescent male and female mice born via caesarean section.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 30;14(1):29807. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-80770-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39616177 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stokholm J, Thorsen J, Blaser MJ, Rasmussen MA, Hjelmsø M, Shah S, et al. Delivery mode and gut microbial changes correlate with an increased risk of childhood asthma. Sci Transl Med. 2020;12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

