Enhancer release and retargeting activates disease-susceptibility genes
- PMID: 34040254
- PMCID: PMC11171441
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-021-03577-1
Enhancer release and retargeting activates disease-susceptibility genes
Abstract
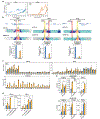
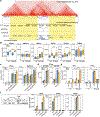
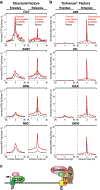
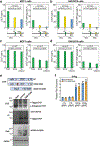
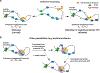
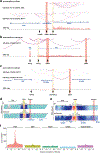
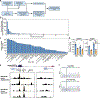
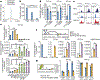
The functional engagement between an enhancer and its target promoter ensures precise gene transcription1. Understanding the basis of promoter choice by enhancers has important implications for health and disease. Here we report that functional loss of a preferred promoter can release its partner enhancer to loop to and activate an alternative promoter (or alternative promoters) in the neighbourhood. We refer to this target-switching process as 'enhancer release and retargeting'. Genetic deletion, motif perturbation or mutation, and dCas9-mediated CTCF tethering reveal that promoter choice by an enhancer can be determined by the binding of CTCF at promoters, in a cohesin-dependent manner-consistent with a model of 'enhancer scanning' inside the contact domain. Promoter-associated CTCF shows a lower affinity than that at chromatin domain boundaries and often lacks a preferred motif orientation or a partnering CTCF at the cognate enhancer, suggesting properties distinct from boundary CTCF. Analyses of cancer mutations, data from the GTEx project and risk loci from genome-wide association studies, together with a focused CRISPR interference screen, reveal that enhancer release and retargeting represents an overlooked mechanism that underlies the activation of disease-susceptibility genes, as exemplified by a risk locus for Parkinson's disease (NUCKS1-RAB7L1) and three loci associated with cancer (CLPTM1L-TERT, ZCCHC7-PAX5 and PVT1-MYC).
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Figures




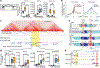
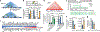
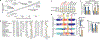
References
-
- Schoenfelder S & Fraser P Long-range enhancer–promoter contacts in gene expression control. Nat. Rev. Genet. 20, 437–455 (2019). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 DK105541/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 GM132778/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK039949/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F32 HD008118/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- DP3 DK112155/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R41 HG008118/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL150521/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL107442/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL156059/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA184770/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK018477/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK039949/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R44 HG008118/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM136922/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- K22 CA204468/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS093066/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG008153/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

