Usefulness of Hybrid Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography/ Computed Tomography in a Case of Ectopic Thyroid Tissue in the Thyroglossal Duct Remnant
- PMID: 34040314
- PMCID: PMC8130679
- DOI: 10.4103/ijnm.IJNM_43_20
Usefulness of Hybrid Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography/ Computed Tomography in a Case of Ectopic Thyroid Tissue in the Thyroglossal Duct Remnant
Abstract
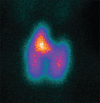
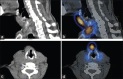
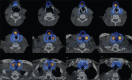
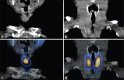
Here, we report a case of a 54-year-old woman affected by thyrotoxicosis, with scintigraphic evidence of a diffuse hyperfunctioning goiter and a large ectopic thyroid tissue in the thyroglossal duct remnant. The latter was apparently more active than the two lobes at 99mTc-pertechnetate scintigraphy, mimicking a condition of preexisting increased sensitivity to thyroid-stimulating hormone stimulation. On the other hand, single-photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography has proven to be a very useful tool in demonstrating this activity to be similar to the thyroid lobes and in defining extension and anatomical relationships of the mass.
Keywords: Ectopic tissue; Graves' disease; single-photon computed tomography/computed tomography; thyroglossal duct remnant; thyroid scintigraphy.
Copyright: © 2021 Indian Journal of Nuclear Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Graves' disease in the cervical thyroid and thyroglossal duct remnant: case report and review of literature.Endocr Pract. 2006 Jul-Aug;12(4):401-5. doi: 10.4158/EP.12.4.401. Endocr Pract. 2006. PMID: 16901795
-
Recurrence of Graves' disease in thyroglossal duct remnants: relapse after total thyroidectomy.Thyroid. 2009 Dec;19(12):1427-30. doi: 10.1089/thy.2009.0143. Thyroid. 2009. PMID: 19916864
-
Graves' disease in a mediastinal mass presenting after total thyroidectomy for nontoxic multinodular goiter: a case report.J Med Case Rep. 2016 Mar 31;10:70. doi: 10.1186/s13256-016-0878-7. J Med Case Rep. 2016. PMID: 27029843 Free PMC article.
-
Radionuclide imaging of the thyroid gland: patterns, pearls, and pitfalls.Clin Nucl Med. 2004 Mar;29(3):181-93. doi: 10.1097/01.rlu.0000114530.12565.5b. Clin Nucl Med. 2004. PMID: 15162989 Review.
-
Imaging of the thyroid in benign and malignant disease.Semin Nucl Med. 2012 Jan;42(1):49-61. doi: 10.1053/j.semnuclmed.2011.07.004. Semin Nucl Med. 2012. PMID: 22117813 Review.
References
-
- Yamauchi M, Inoue D, Sato H, Ashida C, Hiraumi H, Shan L, et al. A case of ectopic thyroid in lateral neck associated with Graves' disease. Endocr J. 1999;46:731–4. - PubMed
-
- Smith TJ, Hegedüs L. Graves' disease. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:1552–65. - PubMed
-
- Filippi L, Schillaci O. SPECT/CT with a hybrid camera: A new imaging modality for the functional anatomical mapping of infections. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2006;3:699–703. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
