Risk of hepatitis B virus reactivation in patients with autoimmune diseases undergoing non-tumor necrosis factor-targeted biologics
- PMID: 34040324
- PMCID: PMC8130042
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i19.2312
Risk of hepatitis B virus reactivation in patients with autoimmune diseases undergoing non-tumor necrosis factor-targeted biologics
Abstract
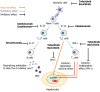
Hepatitis B virus reactivation (HBVr) can occur in patients treated with immunosuppressive medications. Risk stratification for HBVr based on hepatitis B virus (HBV) serology and viral load is an important strategy to determine appropriate HBV monitoring and antiviral prophylaxis use. Recent advances in the understanding of pathophysiology of autoimmune diseases have led the development of cytokine-targeted therapies. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α inhibitors have been widely used for patients with inflammatory bowel disease, psoriasis, and rheumatic diseases. Further, the clinical benefits of interleukin (IL)-12/23, IL-17, or Janus kinases inhibitors have been demonstrated in these patients. It is well known that TNF-α inhibitor use can lead to HBVr, however, the risk of HBVr in patients undergoing non-TNF-targeted biologics have not been fully understood. In this review, we discuss the risk of HBVr in patients treated with non-TNF-targeted biologics, and immunological mechanisms of these medications causing HBVr.
Keywords: Autoimmune diseases; Biological therapy; Hepatitis B virus; Interleukin-17; Interleukin-23; Janus kinases.
©The Author(s) 2021. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Risk of hepatitis B reactivation during anti-TNF therapy; evaluation of patients with past hepatitis B infection.Turk J Gastroenterol. 2020 Jul;31(7):522-528. doi: 10.5152/tjg.2020.19295. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32897226 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis B Virus Reactivation in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Undergoing Biologics Treatment.J Infect Dis. 2017 Feb 15;215(4):566-573. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiw606. J Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 28011918
-
Hepatitis B Reactivation: A Review of Clinical Guidelines.J Clin Gastroenterol. 2021 May-Jun 01;55(5):393-399. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0000000000001520. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 33828065 Review.
-
Pharmacotherapy-Induced Hepatitis B Reactivation Among Patients With Prior Functional Cure: A Systematic Review.Ann Pharmacother. 2019 Mar;53(3):294-310. doi: 10.1177/1060028018800501. Epub 2018 Sep 11. Ann Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 30203666
-
Resolved hepatitis B infection in patients receiving immunosuppressive therapy: Monitor versus prophylaxis against viral reactivation.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Nov 25;101(47):e31962. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000031962. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 36451458 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Infections in the era of immunobiologicals.An Bras Dermatol. 2024 Mar-Apr;99(2):167-180. doi: 10.1016/j.abd.2023.08.004. Epub 2024 Jan 17. An Bras Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38238209 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Inflammatory and Thyroid Hormone Levels Based on Hepatitis A and B Virus Immunity Status: Age and Sex Stratification.Viruses. 2024 Aug 20;16(8):1329. doi: 10.3390/v16081329. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39205303 Free PMC article.
-
Psoriatic Arthritis: The Influence of Co-morbidities on Drug Choice.Rheumatol Ther. 2022 Feb;9(1):49-71. doi: 10.1007/s40744-021-00397-7. Epub 2021 Nov 19. Rheumatol Ther. 2022. PMID: 34797530 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatitis B Virus Reactivation and Mycobacterial Infections Associated With Ustekinumab: A Retrospective Study of an International Pharmacovigilance Database.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jul 4;13:921084. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.921084. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35860015 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis B Virus Reactivation with Immunosuppression: A Hidden Threat?J Clin Med. 2024 Jan 11;13(2):393. doi: 10.3390/jcm13020393. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38256527 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Maini MK, Gehring AJ. The role of innate immunity in the immunopathology and treatment of HBV infection. J Hepatol. 2016;64:S60–S70. - PubMed
-
- Bertoletti A, Ferrari C. Adaptive immunity in HBV infection. J Hepatol. 2016;64:S71–S83. - PubMed
-
- Guidotti LG, Chisari FV. Immunobiology and pathogenesis of viral hepatitis. Annu Rev Pathol. 2006;1:23–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

